Piston Motion
To model the motion of the piston, Simcenter STAR-CCM+ In-cylinder requires specific information about the engine geometry.
Using these geometry properties, Simcenter STAR-CCM+ In-cylinder moves the piston along the negative z-axis, where the offset from TDC position is calculated as:
where:
- is the specified Stroke.
- is the cycle wrapped crank angle in deg (repeats 0 to cycle length).
- is the specified Connecting Rod Length.
- is the specified Pin Offset. See Piston Motion Modification.
is the specified Piston Position Offset. Alternatively, you can specify the Compression Ratio of your engine. In this case, Simcenter STAR-CCM+ In-cylinder calculate as:
where:
- is the cylinder volume at TDC with the valves closed.
- is the specified Bore.
For information on the specified values, see Engine Reference—Cylinder Dialog.
Piston Motion Modification
Simcenter STAR-CCM+ In-cylinder allows you to simulate engines with piston pins and crankshafts that are offset from the cylinder axis. An offset piston pin or crankshaft has the effect of advancing or retarding the piston TDC and BDC position relative to the crank angle.
The pin offset in Simcenter STAR-CCM+ In-cylinder is defined as the distance between the piston pin axis and the crankshaft axis. The sign of the pin offset depends on the rotational direction at the upper half of the crank and on the direction from the piston pin axis to the crankshaft axis.
The following image illustrates the convention that is used for the pin offset sign:
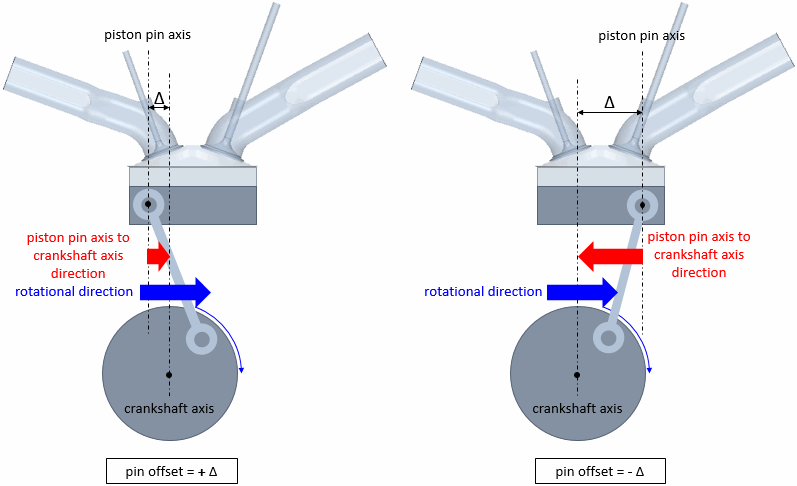
If the two directions are the same, then the pin offset has a positive value. If the directions are reverse to each other, then the pin offset sign is negative.