File-Based Coupling (through Imported CAE Model)
File-based coupling is a method used to couple Simcenter STAR-CCM+ with another CAE code via external files stored in the computer memory.
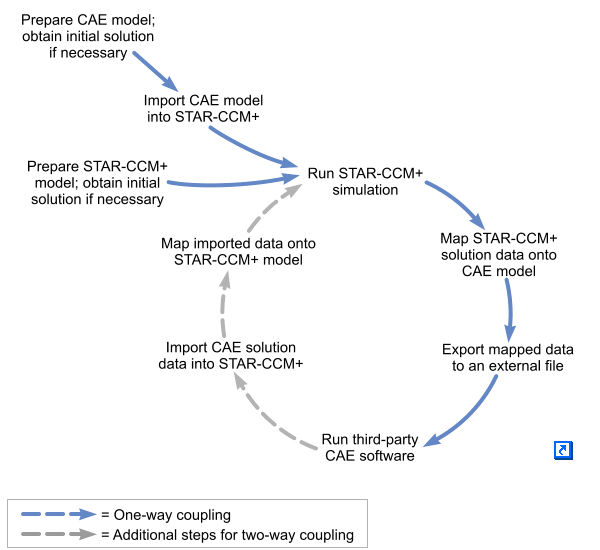
The method allows you to obtain a solution using separate CAE codes to solve for each part of the model, such as the fluid and solid domains in an FSI problem. The powerful set of tools available in Simcenter STAR-CCM+ allow you to import a CAE model into Simcenter STAR-CCM+ and carry out a one-way or two-way coupled simulation.
For one-way coupling, solution data from Simcenter STAR-CCM+ can be mapped onto the CAE model and exported in a format that can be read into the third-party application. The exported data can then be used to specify boundary or operating conditions in the CAE model. An example of this is using Simcenter STAR-CCM+ to compute the conjugate heat transfer solution in the fluid and solid domains of a model, then exporting the solid region temperature solution to an external file. This file can then be read into a third party code, and used to calculate the thermal stresses in the solid. An example of the typical workflow for one-way coupling is shown in the diagram below (solid blue arrows).