Turbulence Suppression Model
The Turbulence Suppression model is a zero-equation model that allows the user to mimic the effect of transition by suppressing the turbulence in a pre-defined region. Since it does not have a predictive capability, it is arguably not a true transition model. However, if the location of transition is known a priori (for instance due to a boundary layer trip), this approach is computationally efficient.
Turbulence Suppression
Turbulence suppression is achieved in a region as follows:
- Setting the turbulent eddy viscosity and/or the Reynolds stresses to zero
- Setting the production terms in the turbulence transport equations to zero
- Not using wall functions to compute wall shear stress or heat flux, but using the laminar flow transport equations instead
Turbulence Suppression Region
One possible approach to define a region in space in which turbulence is suppressed would be to identify an entire region in the volume mesh. However, for certain grid topologies it might impractical to create the appropriate region in the volume mesh.
Instead, the approach taken in Simcenter STAR-CCM+ is to compute two distances for each field point in the interior:
- The wall distance, defined as the distance from a field point to the nearest point on a wall that is not a transition boundary.
- The transition boundary distance, defined as the distance from the field point to the nearest point on a transition boundary.
The region in space in which turbulence is suppressed is then defined as any point at which the transition boundary distance is less than the wall distance. The way in which a turbulence suppression region is created from a transition boundary is illustrated in the following figures.
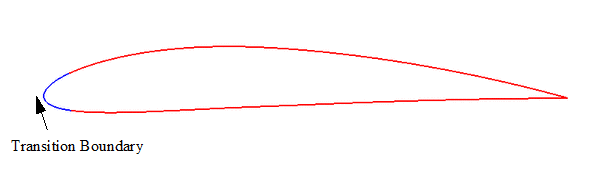

Transition Boundary
A transition boundary is a wall boundary adjacent to which turbulence effects will be suppressed. A wall boundary in a turbulent flow may be turned into a transition boundary by first activating the Transition model in the continuum, and then selecting the turbulence suppression option for that wall. Note that the transition model will have no effect in a physics continuum unless the turbulence suppression option is selected on a wall boundary.
Transition Boundary Distance Calculation
Transition boundary distance is calculated in exactly the same manner as the wall distance, with the proviso that only walls that are transition boundaries are included in the calculation.
The transition boundary distance is computed during solution initialization, and updated only after the mesh or boundary conditions have changed.