Positioning Tool
The Positioning Tool allows you to place Construction Geometries and QuickParts in reference to each other.
The following options are available:
- Align—turns and moves an object until it is aligned with another object.
- Rotate—turns an object around a specified axis.
- Translate—moves an object from one position to another.
The following properties characterize the different positioning options:
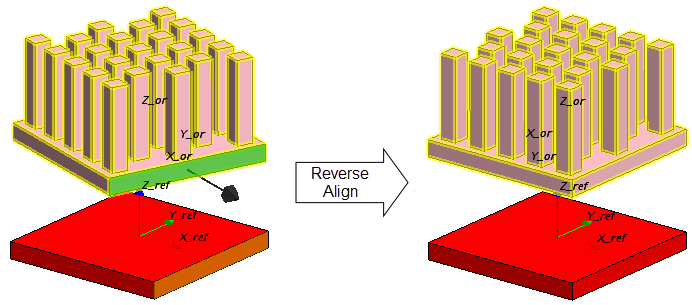
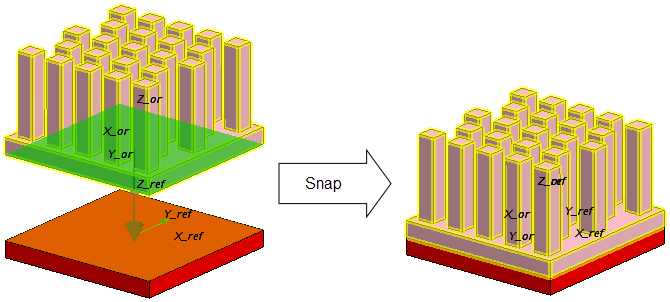
Align—Properties
| Target Objects | Specifies the Construction Geometries or QuickParts you want to align. |
| Align By | Controls the alignment mode. The following options are available:
|
Example: Positioning of a heat sink on a block-shaped chip.
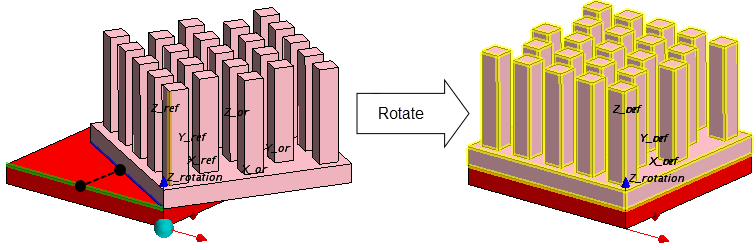
Rotate—Properties
| Target Objects | Allows you to select the Construction Geometries or QuickParts you want to rotate. |
| Rotation Vector | Defines the direction vector of the axis of rotation. The following options are available:
|
| Rotation Position | Defines the origin of the axis of rotation. The following options are available:
|
| Angle | Specifies the angle of rotation. The following options are available:
|
| Coordinate System | Defines the coordinate system for the rotation. You can define the rotation in the Laboratory coordinate system or in the local coordinate systems of another QuickPart. See X_ref, Y_ref, Z_ref in the Graphics window. |
Example: Positioning of a heat sink on a block-shaped chip.
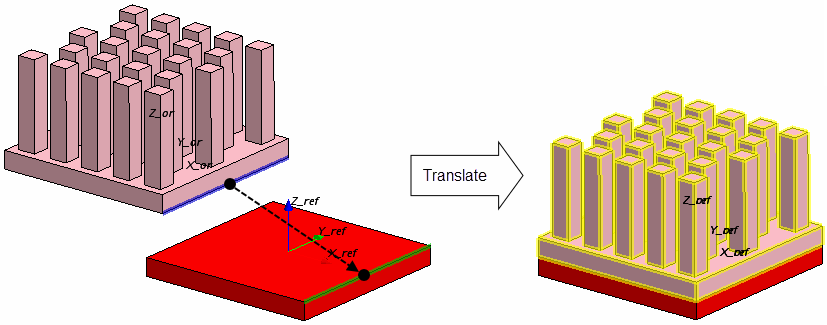
Translate—Properties
| Target Objects | Allows you to select the Construction Geometries or QuickParts you want to translate. | |
| Translation Vector | Defines the direction and distance of translation. The following options are available:
|
|
| Coordinate System | Defines the coordinate system for the translation. You can define the translation in the Laboratory coordinate system or in the local coordinate systems of another QuickPart. See X_ref, Y_ref, Z_ref in the Graphics window. | |
Example: Positioning of a heat sink on a block-shaped chip.