Annotations
Annotations are objects that you add to scenes in order to provide extra information or visualization within the same window. For example, you can show the current time-step in a scalar scene or include a numerical value from a report. Possible annotations include report values, 2D or 3D images, and embedded versions of other scenes.
Adding an annotation is a two-step process as you must first create the template form of an annotation stored within the node, and then you apply a copy of the template annotation in a scene or plot. (Some default annotations already exist in every simulation—you do not need to create these). When an annotation is applied to a scene, a specific node for that annotation appears within the node. In a plot, they appear within the Annotations node.
Once an applied annotation is in a scene or plot, it can only be changed by modifications to its own properties. If you edit the original template annotation subsequently, it does not affect the applied annotation. The exception is the text content of a simple text annotation, which can only be edited from the template.
| Note | The properties of an applied annotation override the properties of the template annotation from which the applied annotation is copied. |
All user-defined annotations can be renamed. Pre-defined annotations cannot be renamed.
Pre-Defined Annotations
- Iteration, Time Step, or Solution Time
- When one of these annotations is added to a scene or plot, Simcenter STAR-CCM+ displays the current value of iteration, time-step, or solution time. Treat these as simple text annotations for positioning, font, and so on.
- Logo
- The logo annotation is similar to a 2D image annotation in that you can import an alternate graphic using the Path property.
- Scene
- The pre-defined scene annotation adds user name, file name, and a time-stamp in the target scene or plot.
User-Defined Annotations
Simcenter STAR-CCM+ allows you to add the following types of annotation:
- 2D Image
-
A 2D image annotation is used to import a graphic into the background of the scene or plot display. The formats that can be imported are PNG, JPEG, TIFF, PNM, and BMP.
Once you have added this annotation to any scene or plot, the picture will appear in the background. Its lower left corner will be set at the center of the display by default.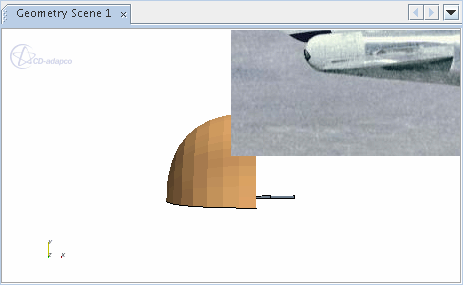
- 3D Image Annotation (Scenes Only)
- The 3D image annotation lets you import an image and position it within three-dimensional space in the scene, rather than in the background of the scene display. This feature facilitates more precise placement of an image near a part of the model.
- Background Image
- A background image functions in a manner similar to that of a 2D image annotation, except with fewer settings. It is useful when you simply want to import a ready-made image into the background of a scene or plot display.
- Derived Data
- A derived data annotation is used to display information about derived data objects that are associated with data set functions.
- Plot Image
- See Scene Image.
- Point Probe
- The visual point probe annotation allows you to annotate the location of a point probe in the scene with the value of a field function. It provides a point probe derived part with a persistent representation in the scene.
- Report Annotation
- A report annotation displays the result of a report as formatted text in the scene or plot display. You create these annotations from the right-click menu of a report rather than from the right-click menu of the node. The text of a report text annotation is refreshed whenever the report itself updates.
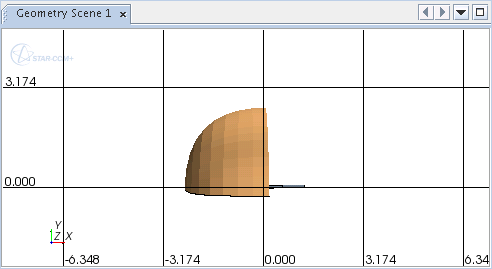
- Scene Grid
- A scene grid annotation lets you add a grid to a scene, allowing easier
interpretation of visual data.
- Scene Image
- Plot and scene image annotations are used to import a plot or a scene as an image in another scene or plot display. The annotation is updated in real-time as the solver is running. The update frequency is controlled by the relevant properties of the destination scene or plot—not the update frequency of the source scene or plot.