Plasma
Plasma is a state of matter similar to a gas that is composed partially or completely of charged particles such as ions and electrons which are not bound to each other.
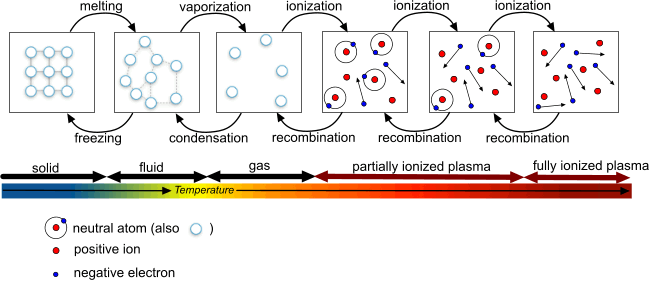
These unbound charged particles are the components of plasma. A gas can display plasma-like properties when only a small proportion of atoms in a sample of the gas are ionized. Electromagnetic fields affect the unbound charged particles—which move collectively as plasma.