Modeling Solar Radiation Loads
Thermal radiative exchange with the solar environment includes both direct and diffuse components.
The direct solar flux is the irradiation from the sun incident directly on the regions without interference from the atmosphere or other objects. Diffuse solar radiation results from the atmospheric scattering, and reflection and transmission from objects such as the ground.
The coordinate system for the orientation of the direct solar flux is defined in the following figure:
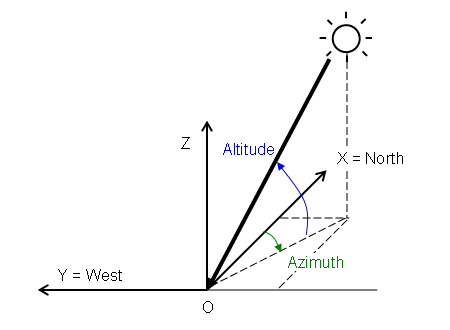
Solar Coordinate System
The X-axis is aligned with the local magnetic north direction and the Y-axis is aligned with the local west direction—that is, the XY plane is the local earth-surface plane. The Z-axis then points skyward since Simcenter STAR-CCM+ employs right-handed coordinate systems.
Thermal radiative exchanges with the environment include only diffuse effects, where the environment surrounding the regions emits diffusively as a blackbody at the environment radiation temperature.
Solar radiative exchanges have a direct and a diffuse component. The direct solar flux is the irradiation from the sun impacting directly on the regions, without interference from the atmosphere or other objects. Diffuse solar radiation results from the atmospheric scattering, and reflection and transmission from objects such as the ground.