Casting Field Functions
The following primitive field functions are available to the casting simulation.
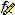 Relative Mass Error Rate
Relative Mass Error Rate
|
The relative mass conservation error rate for all liquid phases in the computational domain. The relative mass error conservation rate is defined as: , where is the target liquid mass that should be in the domain, is the liquid mass that actually is in the domain, and is the current time step. The target liquid mass is given by: where is the mass computed from the previous time step and are the mass fluxes through the boundaries. | |
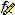 Fluid Side Temperature Fluid Side Temperature
|
The temperature of the fluid-side at a direct Contact Interface or an indirect Mapped Contact Interface between a fluid and a solid region. Useful to evaluate a thermal contact resistance at the interfaces based on the temperature of the melt. The thermal contact resistance can take into account a possible gap formation due to volume shrinkage during solidification. Since the temperatures between melt and mold at the interface usually differ in the range of several 100 K, the regular (averaged) temperature field is impractical. If this field function is evaluated at boundaries other than (mapped) contact interface boundaries between a fluid and a solid region, the regular temperature field is returned. | |
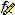 Solid Side Temperature Solid Side Temperature
|
The temperature of the solid-side at a direct Contact Interface or an indirect Mapped Contact Interface between a fluid and a solid region. This is the opposite field function to the Fluid-Side Temperature . If this field function is evaluated at boundaries other than (mapped) contact interface boundaries between a fluid and a solid region, the regular temperature field is returned. | |