Eulerian: Bubble Formation in a Fluidized Bed
This tutorial demonstrates how to model bubble formation in a fluidized bed in Simcenter STAR-CCM+. It simulates the injection of gas into a fluidized bed and monitors the formation and growth of the bubble.
Fluidized beds are formed when a fluid is passed through a solid particulate substance to cause the mixture to flow like a fluid. The formation and propagation of bubbles within the bed affect its heat and mass transfer properties.
The shape of the bubble as well as its quantitative growth has been reported ([970]). The gas injection orifice is 15 mm wide. The superficial gas velocity at the orifice is 10 m/s. The rest of the inlet has a superficial gas velocity of 0.25 m/s; the minimum gas velocity to fluidize the bed. The geometry is shown below.
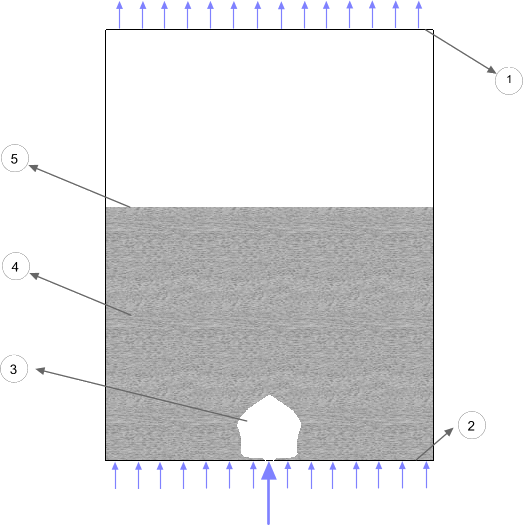
|
Index |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Air outlet |
|
2 |
Inlet with air orifice |
|
3 |
Bubble |
|
4 |
Fluidized bed |
|
5 |
Free surface |