Hybrid Multiphase: Fountain
In Simcenter STAR-CCM+ modeling, the term hybrid multiphase refers to modeling multiple flow regimes of a phase material using a combination of several different multiphase models. This modeling capability widens the range of real life multiphase flows that you can simulate.
In a hybrid multiphase simulation, each multiphase model covers a particular flow regime. The transition of a phase material between flow regimes is handled through phase interactions taking into account local flow conditions and mesh cell size. There are various applications for this type of modeling such as vehicle water management (wind shield wipers, side mirrors), oil jet cooling in electric motors, or multiphase pumps.
In this tutorial, you simulate the flow of a simple water fountain in an open environment. The following screenshot shows the geometry and the different flow regimes manifested in the simulation:
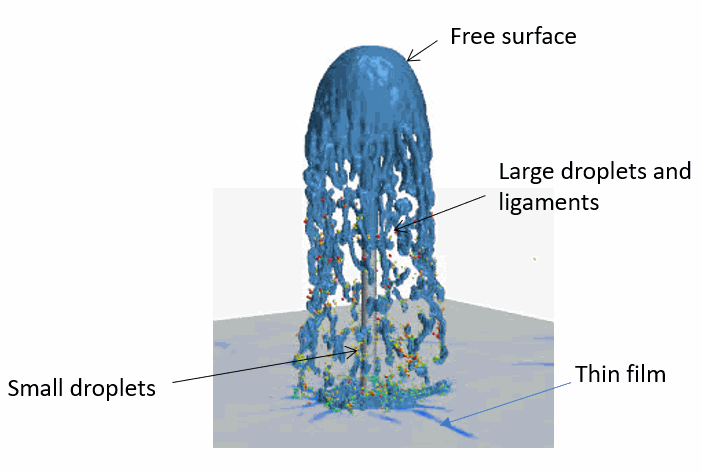
With a velocity of 5 m/s, the free surface water jet exits the cylindrical fountain geometry into the air, thus forming a large-scale interface between water and air. Primary break-up of the jet creates large contiguous water droplets and ligaments. Both of these flow regimes are modeled using the Volume of Fluid (VOF) model.
The large water droplets and ligaments (also known as VOF blobs) break up into smaller water droplets. When the diameter of small spherical water droplets falls below a certain threshold, (here 5 mm), they transition to Lagrangian droplets whose paths are tracked using the Lagrangian Multiphase model. The VOF to Lagrangian conversion is handled by the Resolved Eulerian-Lagrangian Transition phase interaction model. When the Lagrangian water droplets and VOF blobs impinge on the floor, they form thin film puddles that can accumulate to a pool of water. The thin water film is modeled either in an unresolved way by the Fluid Film model or in a resolved way by the VOF model. Based on volume fraction and cell size, the Resolved Fluid Film phase interaction model determines which approach is taken.
Adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) is employed to locally refine the mesh along the water-air free surface. Once a VOF blob has transitioned to a Lagrangian droplet, AMR coarsens the mesh.
This tutorial focuses on demonstrating the workflow for setting up hybrid multiphase simulations. As a result, you create an animation that displays all of the modeled flow regimes.