Advanced Rendering Reference
Within the Scenes node and the Tools node, you can access objects that let you activate and control advanced rendering.
Advanced Rendering Properties
This node provides parameters for advanced rendering capabilities, which you apply to the entire scene rather than to an individual displayer.
- Quality
-
Controls quality of the final image in a range from 0.0 (minimum) to 1.0 (maximum), with higher quality requiring longer rendering time. The time to produce an image depends as well on the complexity of the scene setup, thus simple scenes require less time to render compared to complex scenes with the same quality value. Some effects, such as soft shadows, or more physically correct options like the Metal rendering material, can also require longer render times than, for example, using the simpler Non-Physical material with hard shadows.
- Shadow Override
- Allows overriding displayer
settings for shadow appearance:
- Use Displayer Property: this property is deactivated, leaving the displayer settings in effect.
- No Shadows: deactivates
all shadows in the scene.

- Soft Shadows: enables
shadows and sets Directional Light
Shadow Sharpness to 0.5 on all
displayers, giving all shadows in the scene a soft edge (see Directional Light Shadow Sharpness).

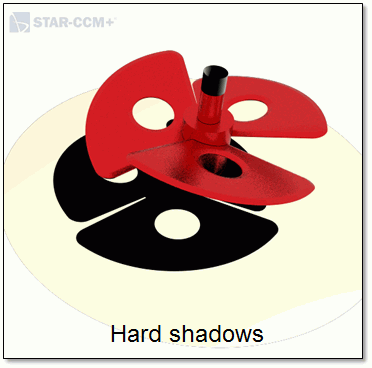
- Hard Shadows: enables
shadows and sets Directional Light
Shadow Sharpness to 1.0 on all
displayers, giving all shadows cast by directional lights a hard
edge.
Note Shadow sharpness only affects the lighting controlled by directional lights that you access in the node, not light-emitting material lighting or lighting effects from the background. Lights from light-emitting materials are area lights that produce shadows naturally. Both distance and geometry size contribute to shadow sharpness: the farther from a shadow caster or the smaller the light-emitting geometry, the sharper the shadow. - Blend Epsilon
- Controls blending, in a range from 0 to 1.0, among the multiple rendering modes that are used with advanced rendering. This parameter helps lines and points to blend correctly in the advanced rendering.
- Min/Max Samples per Pixel
- Specifies the sampling coverage of each pixel. The values set minimum and maximum bounds for samples shot per pixel. The actual number of samples shot per pixel varies depending on the quality settings, but it is always within the bounds set with this parameter.
[displayer] > Advanced Rendering Effects
This node becomes available in a displayer when you activate the Enable Advanced Rendering property of the scene.
- Enable Shadows
- When activated, computes shadowing on part surfaces in the displayer.
- Directional Light Shadow Sharpness
- On a scale from 0 to 1, ranges
from a very soft shadow, to various degrees of softness of shadows, to
completely sharp. For information on setting shadow sharpness for the scene
directional lighting, see Shadow Override.
Note Shadow sharpness only affects the lighting controlled by directional lights that you access in the node, not light-emitting material lighting. Lights from light-emitting materials are area lights that produce shadows naturally. Both distance and geometry size contribute to shadow sharpness: the farther from a shadow caster or the smaller the light-emitting geometry, the sharper the shadow. - Casts Effects
- When activated, the geometry in the displayer participates in the lighting of the scene by casting shadows, and reflecting and refracting light onto other objects. When turned off, the displayer does not interact with the lighting in the rest of the scene at all. It does not cast shadows. It is not reflected in nor does it refract light onto other objects or itself, and it is not visible through refractive surfaces.
- Advanced Rendering Materials
-
This node lets you add special rendering effects. The Advanced Rendering Materials node allows you to use the color that the displayer uses, for example a constant surface color or a scalar value color, and apply additional effects such as the reflection and refraction of the transparent body. This approach differs from using the Preset Material object, which is activated by an entirely separate color mode, Preset Material.
You can access rendering options in the Effect property of this node, listed in the table below.
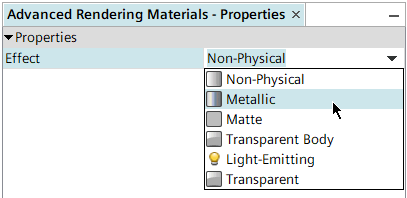
Option Activated Child Nodes - Non-Physical
-
By setting the Reflection and Refraction values greater than 0, you can imitate water. For a more realistic rendering of water, use a Transparent Body rendering material (see Rendering Materials).
- Non-Physical
- This option imitates OpenGL rendering, particularly when the
Absorption property is set to the default value of
1.0.
It provides the following settings:
- Index of Refraction
- The index of refraction (IOR) that is used with the Refraction setting, on a range from 1.0 to ∞.
- Reverse Surface Orientation
- When activated, reverses the direction of the local surface normal vector, for example for a case where the normals point into a surface.
The following settings control the percent contributions, along a range from 0 to 1.0, of surface characteristics:
- Absorption: Surface color
- Reflection: Reflected light
- Refraction: Refracted light
Note Beginning in v12.06, the absorption, reflection, and refraction values can add up to any sum you want. However, for advanced rendering images prepared in versions prior to 12.06, continue to keep these settings summing to 1.0. - Metallic
- Metallic
- Provides the following settings:
- Specular Color
- This color approximates a mirrorlike finish. It is defined by RGB colors.
- Roughness
- Controls the roughness of the surface with a numeric parameter ranging from 0 to 1.0.
- Clearcoat IOR
- Index of Refraction (IOR) of the clearcoat applied to the material, on a range from 1.0 to ∞. (1.0 equals no coat.)
- Matte
- Matte
- Provides the following settings:
- Sigma
- Controls the roughness of the surface, on a range from 0 to 90 degrees. Lower values give the appearance of a smoother surface, while higher values result in a rougher surface.
- Clearcoat IOR
- See the description above for the Metallic option.
- Transparent
- Transparent
- For the effect of a thin-walled fresnel
(glass-like) material, provides the following
settings:
- Index of Refraction
- The index of refraction (IOR) that is used with the Refraction setting, on a range from 1.0 to ∞.
- Transparent Body
- Transparent Body
- For the effect of a volumetric fresnel
(water or glass-like) material, provides the
following settings:
- Index of Refraction
- The index of refraction (IOR) that is used with the Refraction setting, on a range from 1.0 to ∞.
- Roughness
- Controls the roughness of the surface with a numeric parameter ranging from 0 to 1.0.
- Reverse Surface Orientation
- When activated, reverses the direction of the local surface normal vector, for example for a case where the normals point into a surface.
- Light-Emitting
- Light-Emitting
- For the effect of a material that acts as a light source, provides the Intensity setting, on a range from 0.0 to ∞.
Preset Material
This object gives access to predefined materials that you can save and quickly apply to a displayer. The materials are represented by objects in the node. The Preset Material node makes it easier to simulate metals without an RGB color, such as gold or copper, and to record a physically accurate index of refractions.
The Material property of this node lets you select rendering materials using an editor.
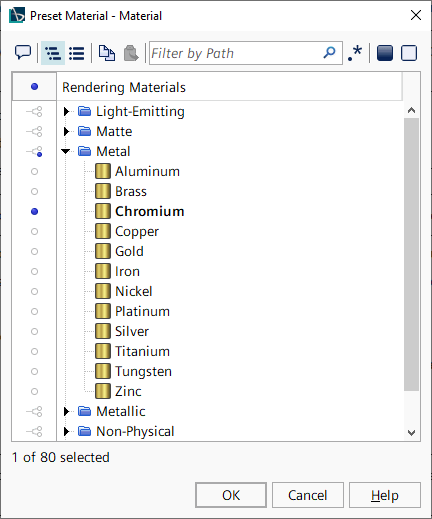
The Preset Material node becomes available in a displayer when the Color Mode property of that displayer is set to Preset Material. When activated, it hides the node. This option is not available for the scalar displayer, which does not have a Color Mode property.
Rendering Materials
This manager node within the Tools node contains the supplied material effects, organized in subfolder nodes by type, with which you can set up your advanced rendering. You can also create your own materials.
| Note | These materials also work in the default OpenGL mode. The material color is always a constant color (OpenGL or advanced rendering). In OpenGL mode however, lights from light-emitting materials do not contribute to the light in the scene. |
The New Rendering Material submenu lets you add a material from among the following types:
- Non-Physical: material simulating simple rendering shading, with options of adding reflection or refraction effects.
- Transparent
Body: material simulating fresnel properties, such
as water or glass. This option produces refraction and reflection based on the
direction of the rays.
Note It is recommended that you use this material only for watertight and/or closed geometry. To ensure accurate results in cases of single sheets of geometry, use Transparent. - Metal: material that realistically simulates metal appearance, such as gold or copper. This material includes actual lighting data from physics sources. See Additional Rendering Materials - Values.
- Metallic: material simulating metal with user-defined RGB color. This material has simpler settings than Metal, and so is more intuitive to edit for adjusting the appearance of the image.
- Matte: material with a diffusely lit appearance (no specular component), such as rubber.
- Light-Emitting: material that acts as a light source, allowing you to add dynamic lighting effects.
- Transparent: material simulating a sheet or shell of a fresnel material. An example would be a car window. A Transparent Body material would treat the car interior as a single solid block of glass.
In addition, each subfolder of the node has a right-click action that lets you create a material of the type represented in that subfolder. For example, the node has the right-click action New Metal Material.
Properties Lookup
The following table shows which properties are used by which material type.
| Note | Beginning in v12.06, the absorption, reflection, and refraction values can add up to any sum you want. However, for advanced rendering images prepared in versions prior to 12.06, continue to keep these settings summing to 1.0. |
| Non-Physical | Transparent Body | Metal | Metallic | Matte | Light-Emitting | Transparent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
 |
 |
 |
||||
|

|
||||||
|

|

|

|
||||
|

|

|

|

|
|||
|

|
||||||
|

|

|
|||||
|

|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|

|

|
|||||
|

|

|

|

|
|||
|

|
||||||
|

|

|
|||||
|

|

|
Additional Rendering Materials - Values
The rendering materials that are listed in this table are not included in Simcenter STAR-CCM+ by default. To add these materials to your simulation:
- Right-click the node and select .
- Rename the new Metal node to indicate your choice of material.
- Enter the corresponding values for the material in the Index of Refraction and Absorption Coefficient properties.
Additional material information is available at the RefractiveIndex.INFO database: https://refractiveindex.info/.
| Metals/Compounds | Index of Refraction | Absorption Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
|
Aluminium (Al) |
(1.65394092, 0.878498793, 0.520122647) |
(9.20430565, 6.25620461, 4.82674885) |
|
Aluminium arsenide (AlAs) |
(3.59736872, 3.22613931, 2.21235132) |
(0.000665507279, -0.000498788548, 0.00740946969) |
|
Aluminium antimonide (AlSb) |
(4.70830059, 4.05196238, 4.57418489) |
(-0.0291775465, 0.0934454054, 1.29783976) |
|
Amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) |
(5.59115076, 4.77824545, 4.89232111) |
(0.227737248, 0.617842078, 1.605533) |
|
Beryllium (Be) |
(4.17617416, 3.1783011, 2.77819276) |
(3.82729554, 3.00373626, 2.86292768) |
|
Caesium Iodide (CsI) |
(2.14034843, 1.69870293, 1.65889668) |
(0, 0, 0) |
|
Copper Oxide (CuO) |
(3.24062014, 2.44260335, 2.20555592) |
(0.519990921, 0.568822145, 0.720639527) |
|
Diamond (d-C) |
(2.90008092, 2.29322004, 2.22275257) |
(0, 0, 0) |
|
Mercury (Hg) |
(2.39383841, 1.43696785, 0.907622635) |
(6.31419611, 4.36266136, 3.41453838) |
|
Iridium (Ir) |
(3.07986569, 2.07777429, 1.61445522) |
(5.58028269, 4.05854368, 3.2603364) |
|
Potassium (K) |
(0.0639137104, 0.0463115685, 0.0381032713) |
(2.09975433, 1.34607041, 0.911276996) |
|
Lithium (Li) |
(0.265251547, 0.195191294, 0.220449701) |
(3.53304243, 2.30618262, 1.66505289) |
|
Magnesium Oxide (MgO) |
(2.08521605, 1.64720988, 1.59149516) |
(4.44628362e-012, -3.69021567e-012, 2.56077087e-011) |
|
Molybdenum (Mo) |
(4.47417498, 3.51799154, 2.77018428) |
(4.10238791, 3.41361785, 3.1439271) |
|
Sodium (Na) |
(0.0601384044, 0.0560220294, 0.061859671) |
(3.17254162, 2.10799718, 1.57574701) |
|
Sodium chloride (NaCl) |
(1.85314035, 1.46401298, 1.41509354) |
(0, 0, 0) |
|
Niobium (Nb) |
(3.41287279, 2.78427768, 2.39050436) |
(3.43407393, 2.73183012, 2.57445478) |
|
Rhodium (Rh) |
(2.58031034, 1.85623479, 1.55113983) |
(6.76788616, 4.69296551, 3.96766329) |
|
Silicon carbide (SiC) |
(3.16561365, 2.52060437, 2.47410822) |
(7.26809503e-007, -6.84328938e-007, 9.99246458e-006) |
|
Silicon monoxide (SiO) |
(2.3598175, 1.89618707, 1.89423704) |
(0.0118285827, 0.023843335, 0.0780569166) |
|
Tantalum (Ta) |
(2.05820084, 2.38801837, 2.6225028) |
(2.40293002, 1.73766804, 1.9429121) |
|
Tellurium (Te) |
(7.37519979, 4.47256279, 2.63149166) |
(3.24919248, 3.51991487, 3.28520942) |
|
Titanium oxide (TiO2) |
(3.44928217, 2.79576182, 2.89899373) |
(0.000102369493, -8.94818368e-005, 0.000633714546) |
|
Vanadium (V) |
(4.26843071, 3.50570178, 2.75527763) |
(3.48376703, 2.88321757, 3.1051085) |
|
Tungsten (W) |
(4.36142588, 3.29329371, 2.99190831) |
(3.49324656, 2.59933424, 2.2683773 |