Filters, and the predicates that define them, drive the search tool.
Every filter that you create must use at least one of the following predicates, and you can use more than one predicate to build up a single filter. Some predicates make use of a grouping mechanism. See
Filters and Predicates Reference: Grouping Mechanisms for more information about the various grouping mechanisms.
| Predicate
|
Description
|
Uses Grouping Mechanism?
|
| Part Name
|
Searches for parts based on their presentation name.
|
No
|
| Part Surface Name
|
Searches for part surfaces based on their presentation name.
|
No
|
| Volume
|
Searches for closed surfaces based on the volume.
|
Yes
|
| Area
|
Searches for faces/surfaces based on the area.
|
Yes
|
| Area/Volume Ratio
|
Searches for faces/surfaces based on the area/volume ratio of the closed surface.
|
Yes
|
| Face Count
|
Searches for faces/surfaces based on the face count.
|
Yes
|
| Topology
|
Searches for closed or manifold surfaces.
|
Yes
|
| Diagnostic Error
|
Searches for
faces/surfaces based on diagnostic errors. For pierced faces, the
number returned with the filter result includes faces that are
adjacent to piercing edges. The corresponding surface diagnostic
only reports the pierced face total. |
Yes
|
| Object Filter
|
Searches using pre-defined filters from the simulation tree.
|
No
|
| Repair Filter
|
Searches using a pre-defined repair filter.
|
No
|
Grouping Mechanisms
Grouping mechanisms are provided when you use spatial-type predicates (for example volume or area). Grouping mechanisms are necessary to provide you some degree of flexibility in determining the collection or subsets of faces that are used for the assessment of the predicate condition. For example, contacts, free edges, and non-manifold edges that exist in a surface change the topology definition (closed or manifold, etc). By using different grouping mechanisms, you can override these geometric conditions without having to directly modify the topology.
Consider the following example:

| Index
|
Description
|
| 1
|
Part A
|
| 2
|
Part B1
|
| 3
|
Part B2
|
| 4
|
Part C
|
| 5
|
Free Edges
|
| 6
|
Non-Manifold Edges
|
| 7
|
Contact
|
In the above example, Part A is closed and is contacting Part B. Part B is open, and split into Part B1 and Part B2, by a non-manifold surface. Part C is open, and vertex-merged with Part B. The following table explains how the grouping mechanisms behave, for this example.
| Grouping Mechanism
|
Number of Groups Identified
|
Topology Breakdown
|
Number of Closed Volumes
|
| Part
|
3
|
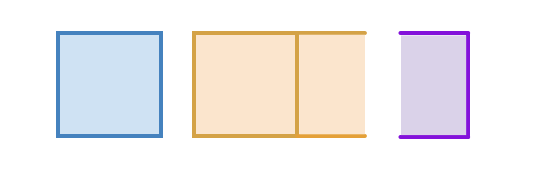
|
1 (Part A)
|
| Contiguous
|
1
|
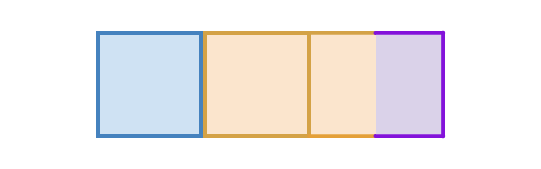
|
0
|
| Volume Topology
|
3
|
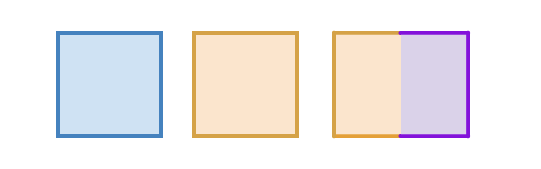
|
3 (Part A,
Part B1,
Part B2 + Part C)
|
| Surface Topology
|
5
|
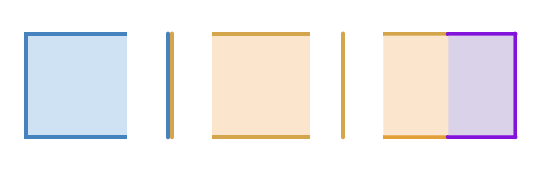
|
0
|
Feedback on the grouping mechanism subsets that are created is provided in the
Output window. You can use this information to help identify unexpected or incorrect filter results. In most cases, the grouping mechanism is most likely the cause of such unexpected results.
Filter Operators
When creating a filter, you can combine multiple search terms together using operators.
| Operator
|
Description
|
| AND
|
This operator assesses each predicate independently based on the starting input and then, the intersection of all the predicate outputs is performed to produce the final result.
|
| OR
|
This operator assesses each predicate independently and returns a match if any of the input criteria are met.
|
| PIPE
|
This operator creates a pipeline (PIPE is shorthand for pipeline) for predicates, where the output of the first predicate is used as the input to the second predicate, and so on.
|
| Note | In some situations, the results from
AND and
PIPE will be identical for the same filter predicate definition, but in other cases, due to the order dependence of the
PIPE predicates, the result will be different. In most cases, the
PIPE operator is generally faster and uses less memory than the
AND operator.
|








