Meshing
A mesh is a discretized representation of a geometric domain. This domain can include real-world geometry, its content, and its surrounding environment.
Simcenter STAR-CCM+ solvers find solutions to physics equations at the locations defined by the mesh. For Finite Volume (FV), Simcenter STAR-CCM+ computes values at cell centers; for Finite Element (FE), Simcenter STAR-CCM+ computes values at element nodes (solid mechanics) or edges (electromagnetism). Simcenter STAR-CCM+ can generate meshes suitable for both types of solver.
The physical space that you want to solve within is called the simulation domain. Generating a mesh typically involves creating a suitable simulation domain. There are two types of flow that require different approaches when creating the simulation domain: internal flow, such as a flow in a pipe, and external flow, such as the flow around and through a car.
In cases where you have highly-complex geometry, such as cars and aircraft, capturing this geometry can be challenging. In cases such as these, the Surface Wrapper is used to simplify and capture a watertight representation of the complex geometry. Regardless of whether you use the Surface Wrapper or not, you typically use the Surface Remesher to remesh the initial surface of a geometry. The initial surface of a geometry is usually made up of triangulated surfaces. This triangulation, also know as tessellation, typically contains highly skewed triangles and is not suitable for generating a high-quality volume mesh. Remeshing improves the overall quality of these surfaces by generating more evenly-sized triangles, which is optimal for the mesh models. The remeshed surface is then used as a foundation for the volume meshes.
In Simcenter STAR-CCM+, the surface and volume mesh can be generated automatically or they can be user-guided.
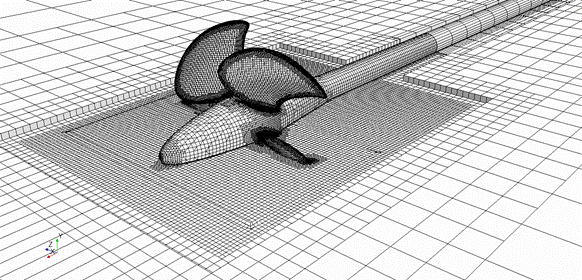
For automatic meshing, Simcenter STAR-CCM+ offers Parts-Based Meshing (PBM) only. PBM detaches the meshing from the physics and provides a flexible and repeatable meshing pipeline. See Parts-Based Meshing for more information.
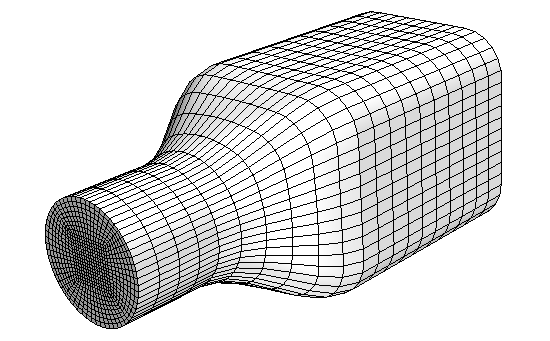
DM generates high-quality, meshes on CAD geometry. This strategy operates by sweeping a surface mesh along a guide surface starting from either the surface of a CAD geometry or a 2D patch mesh through the volume of a part. See Directed Meshing.