Solid Electrolyte Interface Current Density
This section describes the solid electrolyte interface current density formulation.
The Butler-Volmer relationship is used to compute the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) electric current density, which is written as:
(4421)
where:
(4422)
The SEI Surface Overpotential is computed as:
(4423)
The rate coefficient depends on temperature according to:
(4424)
Similarly, the electrical resistance of the SEI is dependent on temperature:
(4425)
The Butler-Volmer relationship is illustrated below:
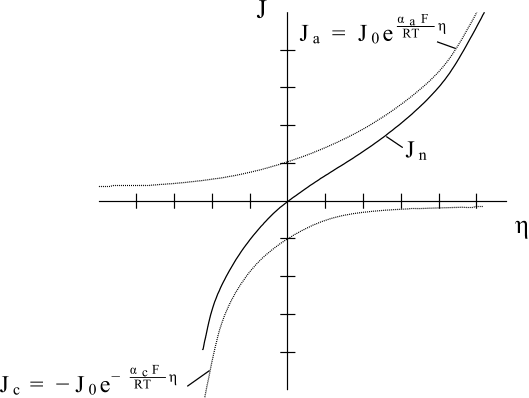
represents the anodic current contribution, while represents the cathodic current contribution to .