Body Motion, Follow Motion, and Superposing Motion
Simcenter STAR-CCM+ allows you to define complex motions with respect to the motion of a 6-DOF body. For example, you can superpose prescribed rotations and translations onto the motion of a 6-DOF body or create a motion that follows the motion of a 6-DOF body in some directions.
Body Motion extracts the motion of the 6-DOF body in order to create some complex motion by superposing additional rotations, translations, or solid displacement.
Superposing motions are mostly used in simulations with multiple regions. An example is a rotating propeller attached to a marine vessel in which the system vessel + propeller moves rigidly in response to the applied fluid forces. Additionally, the propeller has a prescribed rotation motion as shown below:
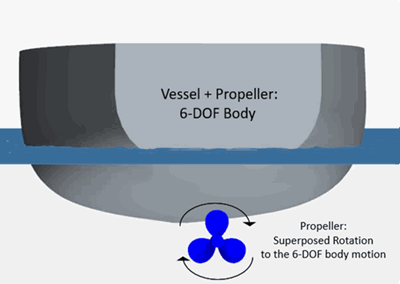
In this case, the fluid region around the vessel moves according to the calculated 6-DOF motion, whereas the fluid region around the propeller moves rigidly according to the calculated motion with the additional prescribed rotation. To realize the propeller motion, you create a Body Motion from the 6-DOF body (vessel + propeller) and superpose a propeller rotation to the body motion. For more details, refer to Adding a Superposed Motion to a 6-DOF Body.
A Follow Motion is always associated to the body for which it was created. It allows you to select the directions in which the follow motion moves with the body. For example, by disabling all rotations, the follow motion only follows the translational motion of the associated body. For more details, see Defining Motion that Follows a 6-DOF Body.
When you model the non-rigid deformations of the propeller using the Solid Stress model, you can optionally set the motion of the surrounding fluid to account for the solid deformations. For more information, see Modeling Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI).