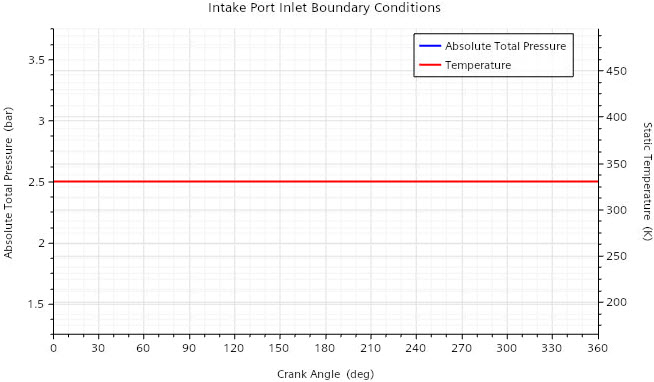
Air enters through the intake port inlet with a static temperature of 330 K
and a pressure of 2.5 bar. At the inlets of the GAVs, you introduce methane gas with a total
temperature of 330 K, where the gas admission starts at 230.0 deg CA and ends at 246.0 deg CA.
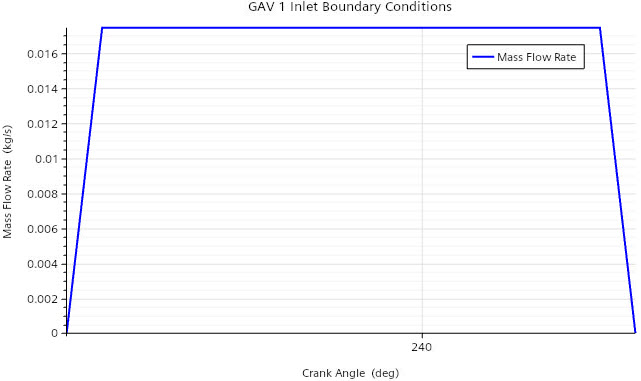
You import a table that describes the mass flow rate of the methane gas as a function of crank
angle. To avoid diffusion of flow quantities at the GAV inlets, you exclude the flow-boundary
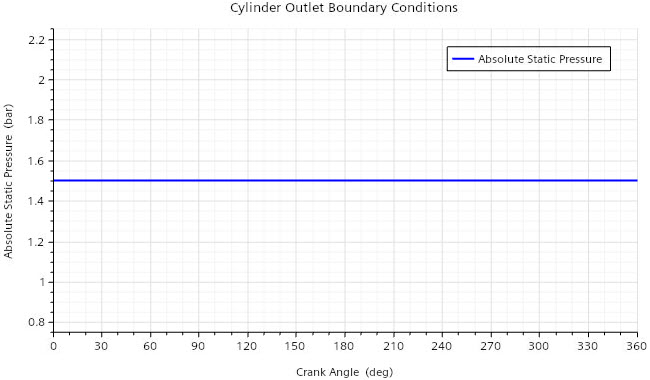
diffusion fluxes. At the exhaust port outlet, you set a pressure of 1.5 bar and a static
temperature of 700 K.
To set the boundary conditions: -
Set the inlet boundary conditions for the intake port:
-
Right-click the node and select Edit.
-
Within the Edit dialog, in the
Pressure group box, click
Import.
-
In the Import Table dialog,
navigate to the inCylinder folder of the downloaded tutorial
files, select twoStrokeEngine_IntaketPort_Inlet.csv, and click
Open.
In the Graphics window, a plot opens that displays the a constant
pressure of 2.5 bar for all crank angles. The correct table columns and units for the
pressure are assigned automatically.
-
In the Static Temperature
group box, from the File drop-down menu, select twoStrokeEngine_IntaketPort_Inlet.
-
Set Temperature Column to T_K.
The plot in the Graphics window
updates to add the temperature data—a constant temperature of 330 K for all crank
angles.
The correct species mass fractions for the inlet are set by default.
-
Click Apply, then Close.
-
Set the inlet boundary conditions for the GAVs:
-
Right-click the node and select Edit.
-
Within the Edit dialog, in the Boundary group box, set
Type to Mass Flow
Inlet.
-
In the Total Temperature
group box, select Constant from the drop-down menu, then set the
constant value to 330.0 K.
-
In the Mass Flow Rate
group box, from the drop-down menu, select Table, then click Import.
-
In the Import Table dialog,
navigate to the inCylinder folder of the downloaded tutorial
files, select twoStrokeEngine_GAV_Inlet.csv, and click
Open.
The correct table columns and units are assigned automatically.
In the Graphics window, a
plot opens that displays the mass flow rate as a function crank angle.
-
In the group box, set the following properties:
| Property |
Setting |
| Air Mass
Weighting |
0.0 |
| Exhaust Mass
Weighting |
0.0 (default) |
| Fuel Mass
Weighting |
1.0 |
-
Click Apply, then Close.
-
Repeat Steps 2 a - f for the node.
-
Exclude the flow-boundary diffusion fluxes:
-
In the Explorer pane, select the Simulation tab.
-
In the simulation tree, expand the node.
-
Select the following nodes in order and deactivate Flow Boundary Diffusion:
- Segregated Flow
- Segregated Fluid Enthalpy
- ECFM-3Z
- Conditional Enthalpy
-
Select the In-Cylinder tab.
-
Set the outlet boundary condition for the exhaust port:
-
Right-click the node and select Edit.
-
In the Edit dialog, in the Pressure
group box, click Import.
-
In the Import Table dialog,
navigate to the inCylinder folder of the downloaded tutorial
files, select twoStrokeEngine_ExhaustPort_Outlet.csv, and click
Open.
In the Graphics window, a plot opens that displays a constant
pressure of 1.5 bar for all crank angles.
-
Click Apply, then Close.
-
Save the simulation
 .
.
 .
.