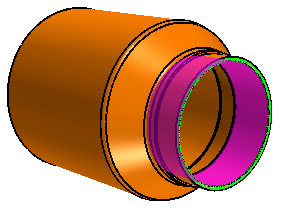
One of the exhaust tips is a sheet body with internal parts. Some of the
surfaces are missing from this part which prevents 3D-CAD from using it as a solid body. In
order to use this body in meshing, you must reconstruct the internal parts before converting
it to a solid body.
To convert the exhaust tip to a solid body: -
First isolate the part for repair:
-
Under the Body Groups node, multi-select the
Exhaust Tip 1, Exhaust Tip 1
2, Exhaust Tip 1 3, and
Exhaust Tip 1 4 nodes.
-
Right-click one of the selected body nodes and select Show
Only.
Before reconstructing the interior, you create a sketch plane
onto which you project one of the perforation holes. You can then use the projected
sketch to recreate the perforation holes once the interior of the exhaust tip is
fixed.
-
To create a sketch plane for the sketch of the perforation hole:
-
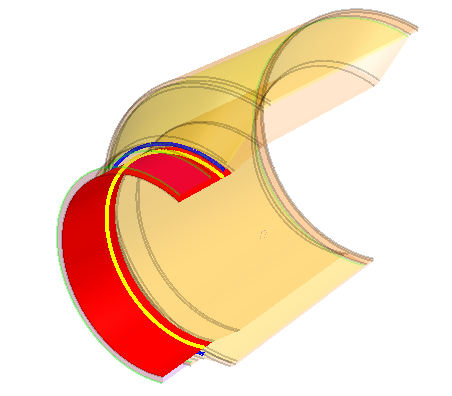
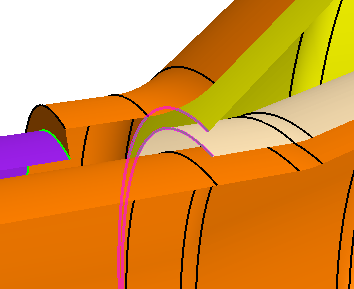
In the graphics window, rotate the part and select the edge that
connects the exhaust tip to the tail pipe as shown in the image below.
-
Right-click the edge and select .
-
In the Plane from Curve panel, click
OK to create the plane.
A sketch plane feature, Plane
2, is added to the Features node.
-
In the 3D-CAD View scene, right-click
the plane and select .
-
In the Plane By Transformation panel,
set Translation Vector to [0.0,
0.0, -0.01]m and click OK.
-
In the toolbar at the top of the 3D-CAD
View scene, click Display Cut Parts using
Multiple Planes.
-
In the Dynamic Sectioning panel,
within Section 1, first select
 (ZX Plane), which
activates a slice through the middle of the exhaust tip.
(ZX Plane), which
activates a slice through the middle of the exhaust tip.
-
In the graphics window, orient the exhaust tip so that reference Plane
3 is closer to you than the middle plane.
-
In the Dynamic Sectioning dialog, now select
 (Reference Plane)
and then, in the graphics window, select Plane 3.
Confirm that you have selected the correct slicing plane by moving the
exhaust tip around in the graphics window.
(Reference Plane)
and then, in the graphics window, select Plane 3.
Confirm that you have selected the correct slicing plane by moving the
exhaust tip around in the graphics window.
-
Click Close.
-
In the Vis toolbar, click
 (Save-Restore-Select Views) and select .
(Save-Restore-Select Views) and select .
-
In the feature tree, right-click the Plane 3
node and select Create Sketch.
-
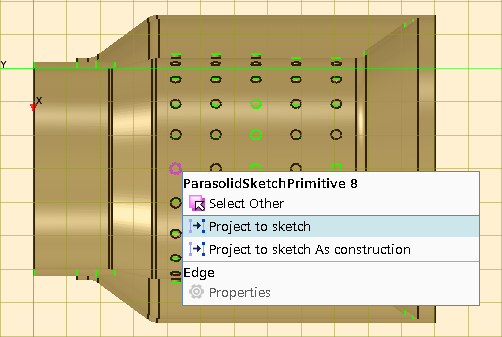
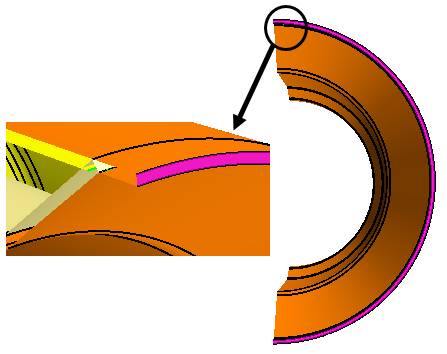
In the graphics window, zoom in closely and right-click the edge of the
hole as shown in the image below and select Project to
sketch.
-
In the Sketch panel, click
OK.
-
Under the Features node, multi-select
Plane 2 and Plane 3,
right-click and select Hide.
The projected perforation hole is used in a later step for
recreating all of the channel holes. Before then, you use the Search Tool to find
the existing channel holes in order to delete them.
-
To create a design filter that finds all the channel faces:
-
To open the Search Tool panel, on the right side of the 3D-CAD View scene, click
 (Show Filter).
(Show Filter).
-
In the Design Filter 1: Input panel,
set Selection Mode to
 (Selected Entities).
(Selected Entities).
-
For Object Type, select
 Bodies .
Bodies .
-
To the right of the Object Type Selection box, click the
 (Object Selector)
and select Exhaust Tip 1. Close the object
selector by clicking the same button as you did when opening it.
(Object Selector)
and select Exhaust Tip 1. Close the object
selector by clicking the same button as you did when opening it.
-
For Input Type, select
 Faces .
Faces .
-
Under the Search Criteria tab, select
the Find Similar option.
-
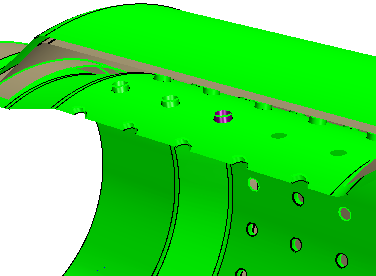
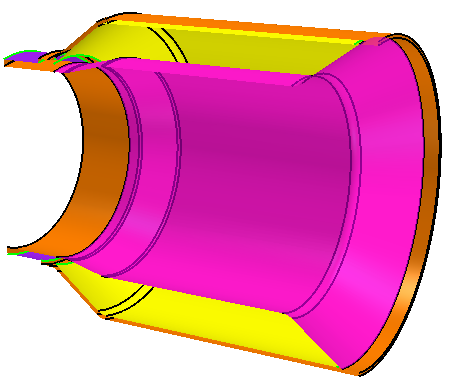
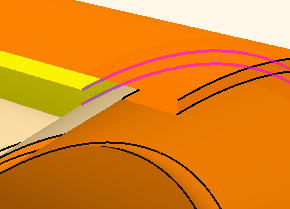
In the 3D-CAD View scene, rotate the
part and zoom in closely to select a channel face, as shown in the
example below.
-
Once you have selected the face, click Search to
locate all the similar faces in the body.
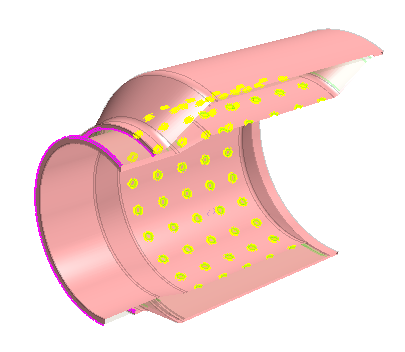
All the channel faces are identified and selected in
the geometry. In total 84 faces are found by the Search Tool.

-
At the bottom of the Filter panel,
click OK.
This action creates Design Filter
1 under the Design Filters node
in the simulation tree.
-
Rename the Design Filter 1 node to
Channel Faces.
-
Use the results from the Search Tool as inputs to the Delete Faces operation:
-
Under the Design Filters node, right click the
Channel Faces node and select
Delete.
-
In the Delete Faces panel, click
OK.
-
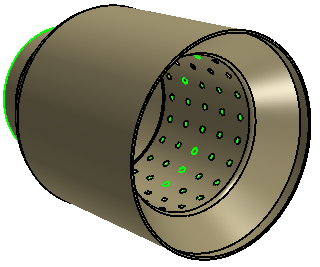
Use the Fill Holes operation to fill the perforation holes:
-
Under the Body Groups node, right-click the
Exhaust Tip 1 node and select .
The operation preview shows that two edges at the entrance
to the exhaust tip are included which are not among the small channel
holes. These edges must be excluded from the fill holes
operation.
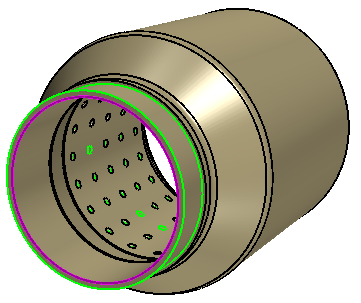
-
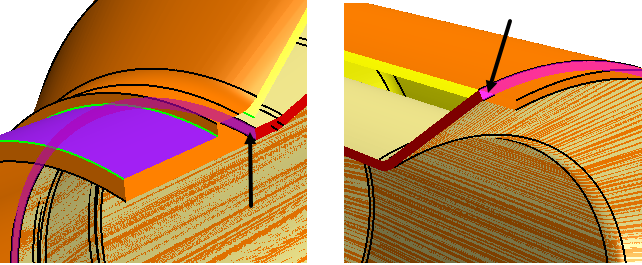
In the Fill Holes panel, click within the
Exclude Holes box and then, in the graphics
window, multi-select the two edges as shown below.
-
In the Fill Holes panel, click
OK to fill the holes.
Due to missing faces, the inner cavity within the Resonator cannot be
formed correctly. To overcome this problem, you first move redundant surfaces and
then recreate the faces that surround the inner cavity.
-
Use the Imprint tool to split the faces where the Exhaust Tip
1 and Exhaust Tip 1 2 bodies intersect:
-
Within the Body Groups node, multi-select the
Exhaust Tip 1 and Exhaust Tip 1
2 nodes, right-click and select .
-
In the Imprint Bodies panel, click
OK.
-
Use the Delete Faces operation to remove unwanted faces inside the exhaust tip:
-
In the toolbar at the top of the 3D-CAD View
scene, change Color Mode to
 (Distinguish Bodies).
(Distinguish Bodies).
-
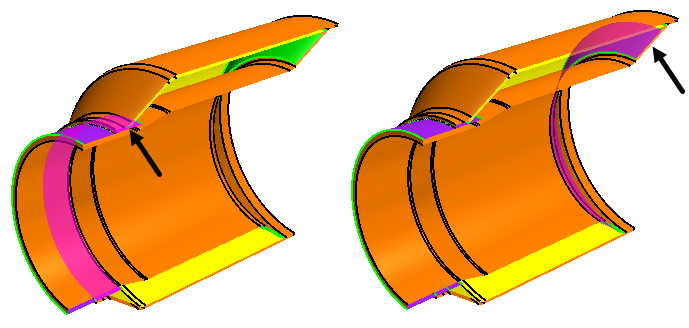
In the 3D-CAD View scene,
multi-select the faces as shown in the images below.
-
Right-click on the faces and select Delete
Faces.
-
In the Delete Faces panel, click
OK.
-
To help in selecting the right portion of the inner surface:
-
Multi-select the inner face at the entrance to the tip and the leading
edge of the floating inner surface as shown below.
-
Right-click the edge or face and choose .
-
In the Split Faces dialog, set Max
Project Distance to 5.0 mm.
-
Click OK.
-
Select the inner surface and create a shell body as follows:
-
Double-click one of the inner faces of the exhaust tip. This action
selects all the faces.
-
While pressing <CTRL>, click the first inner (selected) face at the
entrance to the tip; this action deselects this first face.
-
Right-click one of the remaining selected faces and select
Create Sheet Bodies. In the Create Sheet Bodies panel, click
OK.
Exhaust Tip 1 3 is added
within Body Groups.
-
Right-click and select Thicken.
-
In the Thicken panel, set Direction
to Backward, enter 0.0012m
for Thickness and click
OK.
-
Only the upper surface of the thickened body is required. To delete the other
surfaces:
-
Multi-select the thin faces at each end of the thin body as shown
below.
-
Right-click one of the faces and select Delete
Faces.
-
In the Delete Faces panel, click
OK.
As the single body is now divided, an additional
sheet body, Exhaust Tip 1 5 appears. This body is
the one that you want to keep.
-
Right-click and select Delete. In the
Delete Bodies panel, click
OK.
-
To provide a consistent set of edges for a bridging surface near the outlet of
the tip, create a plane and use it in a boolean slice:
-
Select the face as shown in the image below.
-
Right-click on the face and select .
-
In the Plane By Transformation panel,
enter -0.008925 for the Z component of the
Translation Vector and click
OK.
-
Expand the Body Groups node, multi-select
Exhaust Tip 1 4 and Exhaust Tip 1
5 nodes, right-click and select .
-
In the Slice Panel, set the following
parameters:
| Parameter |
Setting |
| Keep Side
|
Back Side
|
| Sketch Planes
|
Plane 4
|
-
Click OK.
-
Create bridging surfaces at the start and end of the inner volume that you are
forming:
-
Rotate the exhaust tip and multi-select the free edges above the
projected edge that was created from the Split Faces By Edge
Projection tool.
-
Right-click on the edges and select Bridge
Surface.
-
In the Bridge Surface panel, activate
Sew Bodies and click
OK.
-
For the bridging surface near the end of the tip, multi-select the free
edges as shown in the image below.
-
Right-click on the selected edges and select Bridge
Surface.
-
In the Bridge Surface panel, activate
Sew Bodies and click
OK.
-
Under the Features node, right-click on the
Plane 4 node and select
Hide.
-
In the toolbar at the top of the 3D-CAD View
scene, select the
 (Toggle Section
View) icon to deactivate the dynamic sectioning scene.
(Toggle Section
View) icon to deactivate the dynamic sectioning scene.
Exhaust Tip 1 4 is now a solid body
that represents the inner volume of the exhaust tip.
-
Under the Body Groups node, multi-select
Exhaust Tip 1 and Exhaust Tip 1
2, right-click on the nodes and select
Sew.
-
In the Sew Sheet Bodies panel, click
OK.
-
Multi-select Exhaust Tip 1 and Exhaust Tip 1
4, right-click and select .
-
In the Subtract Bodies panel, click
OK.
-
Reconstruct the perforation holes:
-
Rotate the part and select the face inside the exhaust tip as shown
below.
-
Right-click the selected face and select .
-
In the Axis From Resolved Entity
panel, click OK.
-
In the graphics window, right-click the axis and select
Hide.
-
In the features tree, right-click the Sketch 1
node and select Extrude.
-
In the Extrude panel, set the
following properties:
| Parameter |
Setting |
| Direction Type
|
Reverse
|
| Distance
|
0.02973 m
|
| Body
Interaction |
None |
-
Click OK.
-
Under Body Groups, rename the new body to
Perforation Body
-
Right-click the Perforation Body node and select .
-
In the Body Linear Pattern panel, set
the following properties:
| Parameter |
Setting |
| Direction (1) - Distance
|
0.012m
|
| Direction (1) - Number of
Instances
|
5
|
| Body Interaction |
None |
| Create Body Group |
Activate |
-
Click OK.
-
Under Body Groups, rename Body Group
1 node to Perforation
Holes.
-
Right-click the Perforation Holes node and
select .
-
In the Body Circular Pattern Cut
panel, set the following properties:
| Parameter |
Setting |
| Axis Type
|
Set
to Reference Axis and select
Axis 1
|
| Number of Instances
|
20
|
-
Click OK.
-
Multi-select all the feature nodes from Plane 2 to
Circular Pattern Cut 1, right-click on the selected
features and select Group.
-
Rename the feature group to Repairing the Exhaust Tip.
-
Save the simulation.

 (
( (
( (
(



 (
(



 (
(