Before extracting the internal volume, use the Dynamic Sectioning tool to
visually inspect the parts for gaps. Once you have identified the gaps in the geometry, use
the extend solid tool to close them.
-
Right-click a blank area in the 3D-CAD View scene and
select Restore Hidden Bodies.
-
Use the Dynamic Sectioning tool to visually inspect the geometry:
-
In the toolbar at the top of the 3D-CAD
View scene, click Display Cut Parts using
Multiple Planes.
-
In the Dynamic Sectioning panel,
select ZX Plane, set Offset to 0.03 and deselect all the
options for Section 2.
-
Click Close.
-
In the Vis toolbar, click
 (Save-Restore-Select Views) and select .
(Save-Restore-Select Views) and select .
-
If you zoom closely towards the resonator part, you will notice gaps
between the body and its connecting parts.
-
Use the dynamic sectioning tool to visually inspect the remaining
parts. You will notice that there are gaps between each connecting
parts.
The image below shows where the gaps are present in the
geometry.

-
Use the Split Faces tool to project the edge of the tail pipe onto the
resonator:
-
Zoom in closely towards the gap and select the edge of the tail pipe
that lies above the face of the resonator, as shown in the image below.
-
Right-click on the selected edge and select .
-
In the graphics window, select the face of the resonator that is
positioned below the edge.
-
In the Split Faces panel, set
Max Projection Distance to 2.0
mm and click OK.
-
Repeat the steps above to include the edges and faces as shown in the
image below.
-
Repeat the steps above to project the edge from the connecting pipe
onto the muffler. For this operation, in the Split
Faces panel, set Max Projection
Distance to 3.0 mm.
-
Use the Extend Solid tool to fill the gaps:
-
Zoom in closely to visualise the gap between the resonator body and its
connecting parts.
-
Select the face under the tail pipe, as shown in the image below.
-
Right-click on the selected face and select Extend
Solid.
-
In the Extend Solid panel, set Method to Up To Face and
select the face above it for Target Face.
-
Click OK.
-
Repeat the steps above for the remaining gaps.
Once you have filled all the gaps, you use the extract
internal volume to create a fluid volume.
-
To carry out an internal volume extraction:
-
In the toolbar at the top of the 3D-CAD View
scene, select the
 (Toggle Section
View) icon to deactivate the dynamic sectioning scene.
(Toggle Section
View) icon to deactivate the dynamic sectioning scene.
-
At the bottom of the 3D-CAD View
scene, select the
 (Face Feature) menu
and select Extract Internal Volume.
(Face Feature) menu
and select Extract Internal Volume.
-
Click the
 (Object Selector)
icon on the right of the Enclosing Bodies box.
(Object Selector)
icon on the right of the Enclosing Bodies box.
-
In the Object Selection panel, select all the
bodies, then click the
 icon again when done.
icon again when done.
-
To hide the color of the enclosing bodies, right-click inside the
Enclosing Bodies box and select Hide
on scene.
-
Click within the Inlet/outlet Edges or Faces box
and select the following faces:
- The inlet face of the resonator
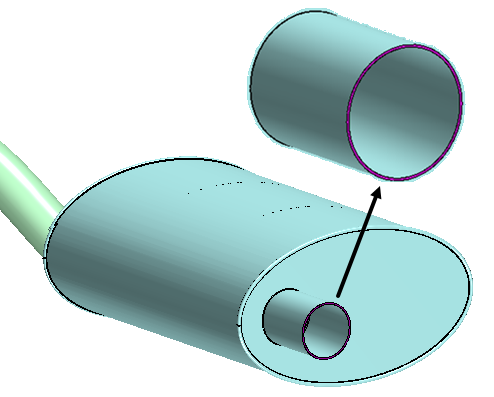
- The outlet faces of both exhaust tips
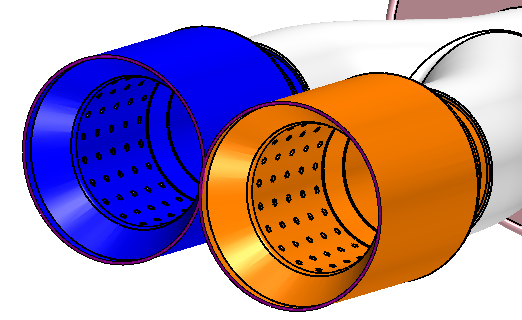
Once you have selected
the faces, normally a preview of the solid body appears in the
3D-CAD View scene when an
internal volume is found. For this case, the preview is not shown
which indicates that there might be a leak in the geometry. To
identify leaks:
-
Switch the Extraction Mode to
 (Detect Leaks
and Extract Liner).
(Detect Leaks
and Extract Liner).
-
In the 3D-CAD View scene, follow the
leak path to the muffler.
-
In the graphics window, zoom in closely towards the leak, then hold the
CTRL key and select the edge of the hole.
The image below shows the leak path to the muffler and if
you zoom in closely you will find the leak hole.
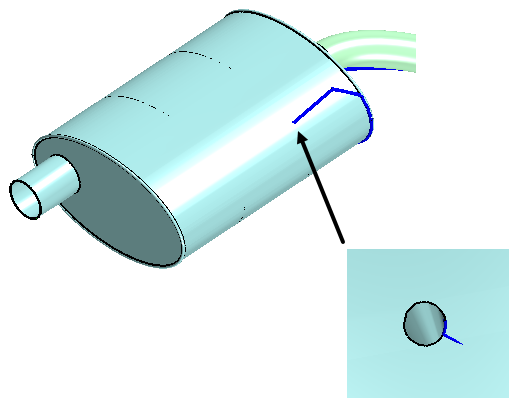
When no further leaks are detected, a yellow
preview of the solid body is shown in the scene.
-
Switch the Extraction Mode to
 (Extract
Internal Volume).
(Extract
Internal Volume).
-
Click OK to proceed with the volume extraction.
-
Multi-select all the new feature nodes, then right-click on the selected
features and select Group.
-
Rename the feature group to Extracting Internal Volume.
-
Save the simulation.

 (
(







 (
( (
( (
(

 (
(
 (
(