Lighthill Wave Model
The Lighthill Wave model provides an efficient method to model sound generation and propagation for incompressible fluid flow ( ).
To calculate the sound propagation in either quiescent or turbulent flows, the Lighthill Wave model introduces a separate wave equation. This equation solves for the transport of the Lighthill pressure , which can be represented as the sum of acoustic pressure and hydrodynamic pressure .
A scale-resolving simulation, such as LES or DES, is coupled (one-way) with the Lighthill Wave model. By adopting this hybrid CFD/Computational Aeroacoustics (CAA) approach, the Lighthill Wave model produces better results (with fewer spurious effects) than a pure compressible flow simulation.
The Lighthill wave model is intended for studying the noise in regions where the contribution of the turbulent fluctuations can be neglected (see red region in the image below):
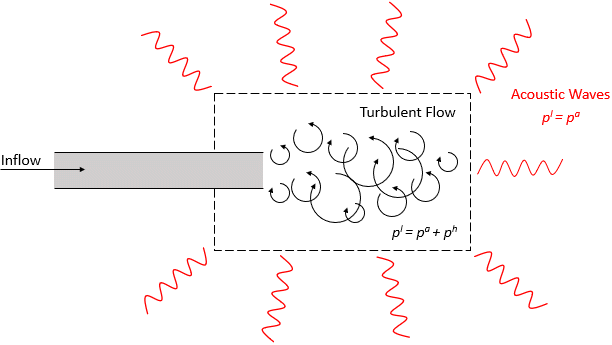
For a practical example of a Lighthill Wave simulation in Simcenter STAR-CCM+, refer to the following tutorial:
Lighthill Wave and Perturbed Convective Wave Modeling: Simplified HVAC Duct