Performing the Spectral Analysis
Using Fast Fourier Transforms, you can determine sound pressure as a function of frequency at each of the point receivers.
To perform the spectral analysis.
-
Right-click the node and select .
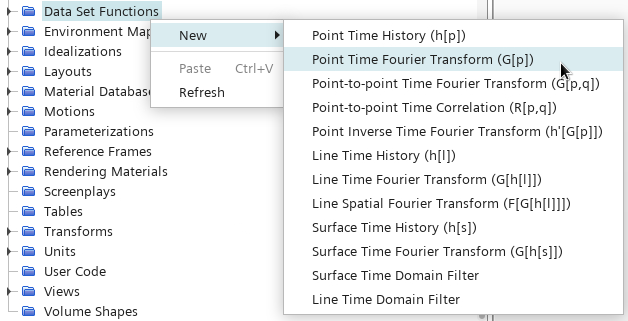
-
Select the G(p) 1 node and set the following properties:
Property Value Start Time 0.02 s Cut-off Time 0.0533 s Amplitude Function Sound Pressure Level Analysis Blocks 2 Overlap Factor 0.5 Window Function Hann - Right-click the node and select .
- Rename the node to derived monitor-back.
-
Select the derived monitor-back node and set Input data 1 to .
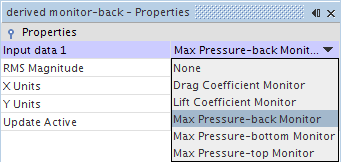
- Right-click the node and select for a second time.
- Rename the entry to derived monitor-bottom.
- Select the derived monitor-bottom node and set Input data 1 to .
- Right-click the node and select for a third time.
- Rename the entry to derived monitor-top.
-
Select the derived monitor-top node and set Input data 1 to .
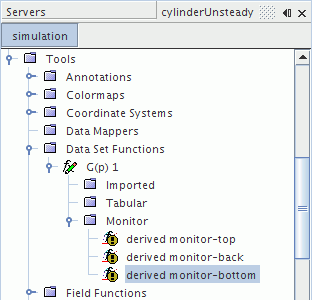
- For each of the derived monitor nodes, activate the Update Active property.
- Rename the node to FFT-SPL.
You now add the derived monitor nodes to a monitor plot.
- Right-click the node and select .
- Rename the node to Monitor Plot - SPL.
- Right-click the node and select Add Data.
-
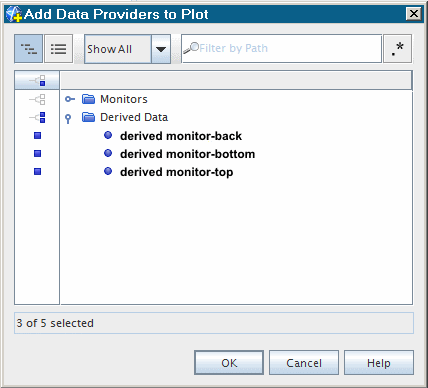
In the Add Data Providers to Plot dialog,
expand the Derived Data node and select the following:
- derived monitor-back
- derived monitor-bottom
- derived monitor-top
-
Select the node and set the following properties:
Property Value Logarithmic Activated Minimum 10 Maximum 20000 - Select the node and set Title to Frequency (Hz).
- Select the node and set Title to Sound Pressure Level (dB).
A scene similar to the one shown below is displayed.
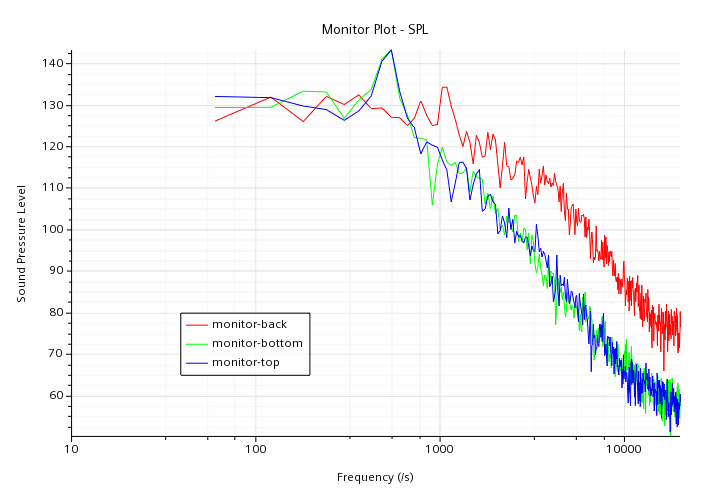

From the above monitor plots, it is seen that there are two peaks: one at 500 Hz for the top and bottom probes (lift mode) and one at 1000 Hz for the back probe (drag mode).
- Select , enter cylinderUnsteady_FFT.sim as the File name, then click Save.