Curve-Fitting the Non-Linear Model Parameters
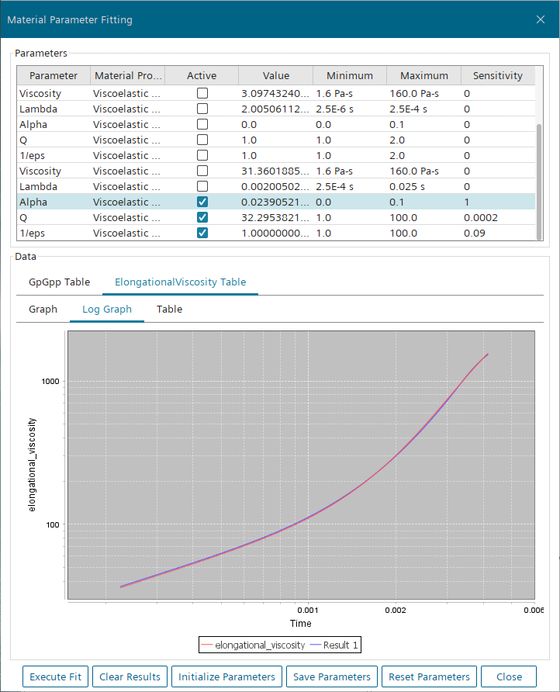
Now you fit the non-linear model parameters , , and using the experimental uniaxial elongational viscosity versus time curve. To obtain an initial value for the relaxation time, you invert the extension rate at which the uniaxial elongational viscosity versus time curve is measured.
To curve-fit the non-linear model parameters:
- Right-click the Material Calibration node and select Fitting Tool....
- Deactivate all parameters in the Parameters list.
- Select the Log Graph tab on the ElongationalViscosity Table pane.
-
Find the viscoelastic mode that has the most influence on the shape of the
curve:
- Click Save Parameters.
- Click Close.
- Examine the values under and note the changes from the initial values.
- Save the simulation.