Setting Boundary Conditions
Boundary conditions define the solved-for quantities—or how the solver is to treat them—around the perimeter of the computational domain. Here, you set boundary conditions for the inlet and wall boundaries.
To achieve a Mach number of approximately 0.75 at the inlet, isentropic relations were used to determine the inlet total pressure and outlet static pressure for a given total temperature. For an outlet static pressure equal to one atmosphere (absolute) and a static temperature of 300 K, the inlet total pressure is 164,904 Pa (absolute). The inlet total temperature is 344.8 K.
The boundary values are specified as gauge pressures. Therefore, using the default reference pressure of 101,325 Pa (one atmosphere),you set the inlet total pressure to 63,579 Pa (gauge). The outlet static pressure is 0 Pa (gauge), the default value.
To set the inlet condition:
- Expand the node.
-
Expand the node, and select the Total Pressure node.
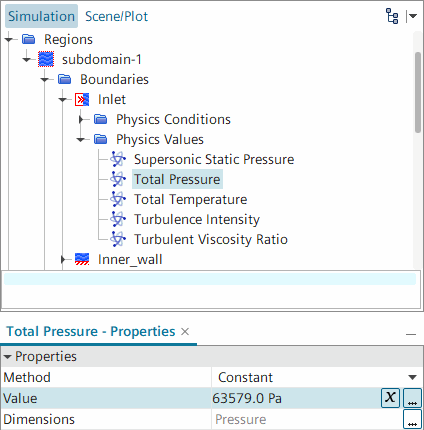
- Set Value to 63579 Pa.
The total pressure setting is relative to the operating pressure value of 101,325 Pa. A supersonic static pressure is also required as part of a stagnation inlet condition but is only used if the inlet velocity becomes supersonic at some instance during solution iteration. The default value of 0.0 Pa relative pressure is sufficient as long as supersonic flow does not occur.
- Within the same Physics Values node, select the Total Temperature node and set Value to 344.8 K.
-
To set the slip wall condition: