Solar Radiation
Thermal radiative exchange with the solar environment includes both direct and diffuse components.
The direct solar flux is the irradiation from the sun incident directly on the regions without interference from the atmosphere or other objects. It is modeled as a collimated source as given by in Eqn. (1701). Diffuse solar radiation results from the atmospheric scattering, and reflection and transmission from objects such as the ground. It is modeled as a diffuse source in Eqn. (1701).
The coordinate system for the orientation of the direct solar flux is defined in the following figure:
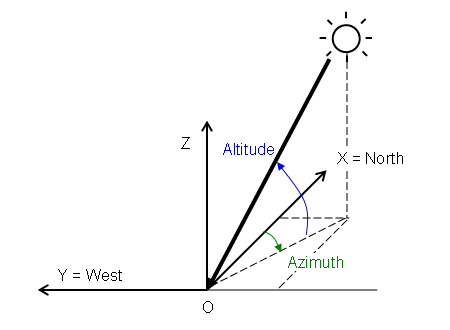
The X-axis is aligned with the local magnetic north direction and the Y-axis is aligned with the local west direction—that is, the XY plane is the local earth-surface plane. The Z-axis then points skyward since Simcenter STAR-CCM+ employs right-handed coordinate systems.
User Input Range for the Solar Calculator
The solar calculator is a set of equations that calculate the astronomical relationship between sun, earth, and the atmosphere. It is developed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) [420]. This formulation presents the equations for solar position and flux calculations in the solar calculator. The user inputs for various parameters must lie within the ranges that are shown in the following table .
All angles that are shown in this formulation are in degrees.
| Variable | Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Year | 1950-2050 | |
| Month | 1-12 | |
| Day | 1-31 (depending on the month) | |
| Hour | 0 – 23 | |
| Minute | 0-59 | |
| Time zone | -12.0 -+12.0 (in hours) | |
| Latitude | - 90.0-+90.0 (in degrees) | |
| Longitude | -180.0-+180.0 (in degrees) | |
| Fraction for diffuse flux | 0.0-1.0 | |
| Sunshine factor | 0.0-1.0 |
Calculation of Sun Direction
Solar altitude, azimuthal angles, and related geometric parameters can be calculated as:
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) in hours:
Julian day [423]:
Time that is used in calculation of elliptical coordinate [423]:
Mean longitude [423]:
Mean anomaly [423]:
Elliptic longitude [423]:
Obliquity of the elliptic [423]:
Declination [423]:
Right ascension [423]:
Greenwich mean sidereal time [423]:
Local mean sidereal time [423]:
where is the user-defined longitude of the geographical location.
Hour angle [423]:
Solar zenith and altitude angles without refraction [423]:
where is the user-defined latitude of the geographical location. is limited to 9 degrees below the horizon to compensate for refraction.
Altitude:
Solar azimuthal angle [423]:
Application of Refraction Correction
The refraction correction [424] is applied as follows:
is the correction factor due to atmospheric refraction.
where equals 1013 millibars atmospheric pressure and equals mean atmospheric temperature.
Refraction corrected altitude:
Refraction corrected zenith:
Calculation of Solar Fluxes
Total solar flux:
where is the solar constant, equal to 1376.0 , and is the sunshine factor.
Diffuse flux:
where is the diffuse factor.
Direct flux: