Normal Modes Solver: Wind Turbine Blade
In solid mechanics, normal modes describe the oscillating motion of a solid body at a set of fixed frequencies, known as natural (or resonant) frequencies of the body.
When a solid structure is subject to a periodic force that acts at the solid resonant frequencies, the amplitude of oscillation is amplified. In extreme cases, this amplification can lead to permanent deformation or fracture of the solid. The calculation of normal modes is essential in engineering applications that model structures that are subject to vibrations, such as suspension bridges and aircraft wings.
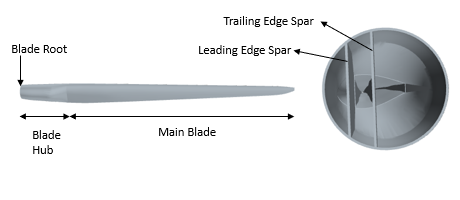
In the simulation, you model the blade as an isotropic, linear elastic solid. The simulation domain includes two solid regions—one for the blade hub and main body, and one for the spar components. The spars and the blade hub are constrained at the root in all degrees of freedom. The simulation is steady-state.