Using 2D and 3D Curves in 3D-CAD
You can import and use 2D and 3D curves in 3D-CAD.
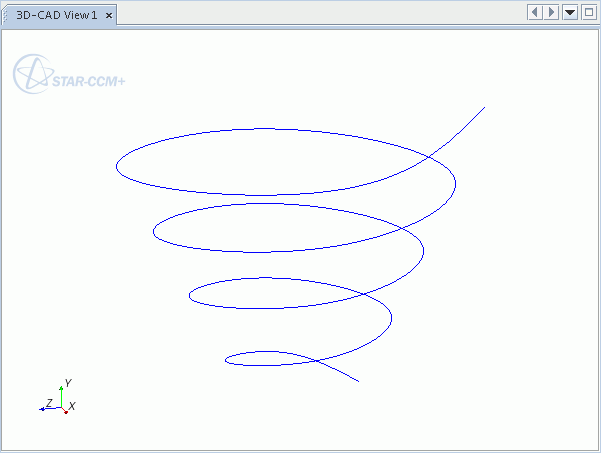
A 2D curve is a sketch entity constrained to a 2D plane (sketch plane), while a 3D curve is not constrained to any 2D plane. A simple example of a 3D spiral is shown below.

You can import curves in 3D-CAD to perform the following operations:
- Extrusions: You can use a closed curve to form a solid body, or an open curve to form a sheet body.
- Sweeps: You can use curves both as profiles or as path curves while creating a Sweep feature. For a curve to be used as a profile, it can be closed (to form a solid body), or open (to form a sheet body). For it to be used as a path, it must be an open curve.
- Lofts: You can use two or more curves (or a combination of curves and planar sketches) to create a Loft feature. For a curve to be used as a profile, it must be closed (to form a solid body), or open (to form a sheet body). For it to be used as a guide wire, it must be an open curve. A Pierce constraint can be used to connect profiles to guide wires—profiles and guide curves must intersect. See Pierce Constraint.
You cannot use 3D curves with the Revolve feature. Composite curves that contain sharp edges are not supported. 3D curves that you import are fully editable. 2D curves are imported as sketches on the XY sketch plane and are fully editable. You can reposition the sketch onto a transform sketch plane if required.
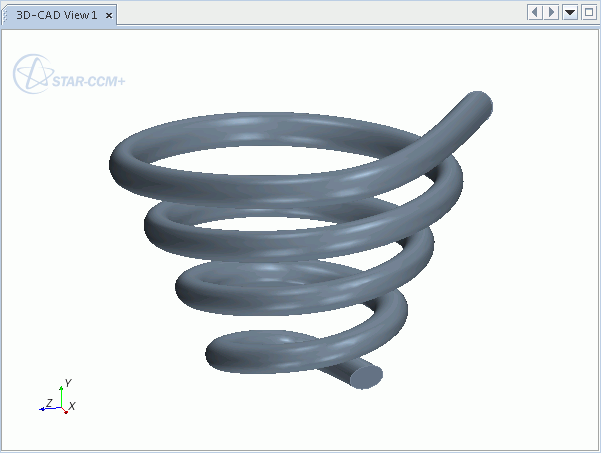
An example of a sweep using a 3D curve is shown below, whereby it is used as the path for the sweep feature.