Defining Lagrangian Phases
A Lagrangian phase is used to define the solid particles in the simulation. The phase requires specific physics models and properties to characterize its behavior. In this case, the solid particles are grains of wheat, with the material properties defined manually.
- Right-click the manager and select .
- Rename the phase as Grain.
- Right-click the manager and select .
-
In the
Grain Model Selection dialog, select the following models, in order:
Group Box Model Particle Type DEM Particles Optional Particle Forces Pressure Gradient Force (selected automatically) Material Solid Equation of State Constant Density Particle Shape Composite Particles - Click Close.
To define the material properties for the Grain particles:
- Select and rename the node to Wheat.
-
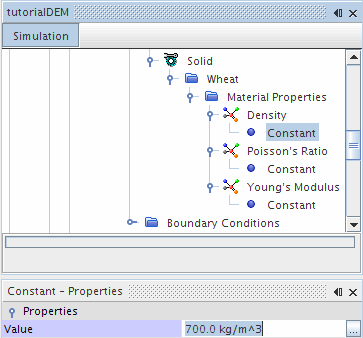
Select the
node and set the
Value to
700 kg/m^3.
-
Set the remaining properties as follows:
Property Setting Poisson's Ratio 0.5 Young’s Modulus 0.2 MPa
To define the physical shape of the grain particles:
- Right-click the node and select .
-
Select the
node and set the
Radius to
0.8.

-
Create two more shapes with the following properties:
Node Property Setting Sphere 2 Position [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] Radius 1.0 Sphere 3 Position [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] Radius 0.8 - Right-click the node and select .
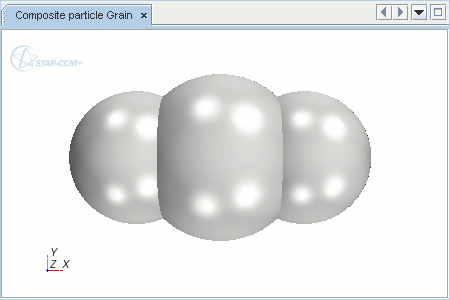
A representation of the grain particle is shown in the
Graphics window.

- Close the Composite particle Grain scene.
To define the physics conditions on the particle boundary:
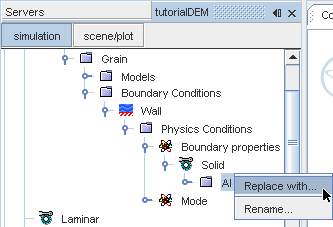
-
Right-click the
node and select
.
-
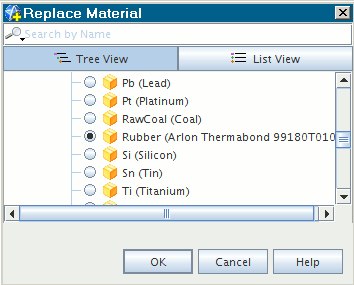
In the
Replace Material dialog, expand the
manager, select
Rubber (Arlon Thermabond 99180T010) and click
OK.
-
Select the
node and check that the
Active Mode property is set to
.
- Save the simulation.