Point-to-Point Time Fourier Transforms
You use Point-to-Point Time Fourier transforms to determine the correlation between two input signals. This data set function applies a Fourier transform to each of the input signals, then performs a convolution on both resulting transforms.
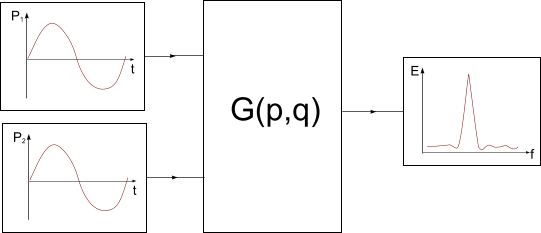
Point-to-Point Time Fourier Transform Properties
|
Update Interval |
Sets the number of time-steps after which to update the Fourier transform. |
|||
|
Filter Type |
Specifies the type of filter that is applied. Digital filters allow you to filter out parts of a signal which correspond to certain frequencies. |
|||
|
None |
Does not use a filter. |
|||
|
Band pass filter |
Keeps frequencies between low and high cut-off levels. Adds an Ideal Filter sub-node in which you can set these levels. |
|||
|
Band stop filter |
Discards frequencies between low and high cut-off levels. Adds an Ideal Filter sub-node in which you can set these levels. |
|||
|
Frequency Function |
Specifies the frequency function that is generated. All these functions are standard functions for this type of analysis. |
|||
|
Frequency |
Frequency in Hz. |
|||
|
Octave Bands |
Discrete frequency bands corresponding to different octaves within hearing range. Each successive band represents twice the range of the previous one. |
|||
|
3rd Octave Bands |
Discrete frequency bands corresponding to one-third of each octave within hearing range. |
|||
|
Fourier Mode |
The index in the Fourier calculations. |
|||
|
Strouhal Number |
The non-dimensional version of the Frequency option. Selecting this option adds a Strouhal Number sub-node to the FT node. |
|||
|
Custom Bands |
Lets you define a set of custom frequency bands by adding a Custom Bands sub-node to the FT node. |
|||
|
Start Time |
The start time of the time sampling for this object. |
|||
|
Cut-off time |
The end time of the time sampling for this object. Clicking the
|
|||
|
Amplitude Function |
Specifies the amplitude function that is generated. All these functions are standard functions for this type of analysis.
|
|||
|
Cross Spectral Density |
The power spectral density of the cross-spectrum signal, (see Eqn. (500)). This option is comparable to the auto-spectral density of 1-point Fourier transforms, (see Eqn. (499)). |
|||
|
Cross Root Mean Square |
The root mean square of the Cross Spectral Density. This option is comparable to the RMS of 1-point Fourier transforms. |
|||
|
Coherence |
in Eqn. (506).A measure of the correspondence between the magnitude of two signals at different frequencies. Its range is 0 - 1. |
|||
|
Phase |
in Eqn. (505). A measure of the offset (phase difference) between two signals. Its range is -p to +p. |
|||
|
Analysis Blocks |
Specifies the number of analysis blocks (see Eqn. (523)) for this data set function to use. |
|||
|
Overlap Factor |
Sets the overlap factor (see Eqn. (523)) between blocks, if any, in a range from 0 to 0.9. This property allows for smooth transitions between blocks. |
|||
|
Window Function |
Specifies the window function applied to the FT. The window function makes the signal periodic: it is guaranteed to be zero at both start and end. For most cases, apply a window function to a signal before applying an FT for best results. Available options:
|
|||
 property customizer button in the right-hand column activates a property customizer that lets you specify both the time value and the appropriate time units (
property customizer button in the right-hand column activates a property customizer that lets you specify both the time value and the appropriate time units (