Coordinate Systems
Coordinate systems are used to specify spatial vectors, such as position and direction for boundary and region values, initial conditions, and properties of location and direction for derived parts. Coordinate systems are also used to define the position of sketch planes in 3D-CAD. For simple applications, the default laboratory coordinate system is sufficient. However, more complex situations can benefit from the definition and use of a local coordinate system or a block-mapped coordinate system.
In Simcenter STAR-CCM+, any coordinate system is represented by a node under .
Laboratory Coordinate System
The laboratory coordinate system is represented by the Laboratory node. This node contains a child node, Local Coordinate Systems, that is used to manage all local coordinate systems (and their derived systems) within the simulation.
Local Coordinate System
A local coordinate system can be defined in terms of Cartesian, cylindrical, or spherical coordinates and can take either the base laboratory coordinate system, or a previously defined Cartesian local coordinate system, as the reference system. A local coordinate system can also be exported from a sketch plane in 3D-CAD for use in Simcenter STAR-CCM+.
Local coordinate systems can be accessed by derived parts and reports, and also serve as scalar and vector field functions. Examples of how they can be used are:
- Initializing the velocity in a region to solid body rotation
- Providing a swirling inlet velocity profile
For more information on Cartesian, cylindrical, and spherical coordinate systems, see the Theory Guide section Coordinate Systems. When defining coordinate system parameters, you can specify an expression that references other quantities within the simulation, including global parameters. If you are working in conjunction with a CAD Client, then the expressions can also reference CAD parameters and CAD responses (only in Simcenter STAR-CCM+ Client for NX).
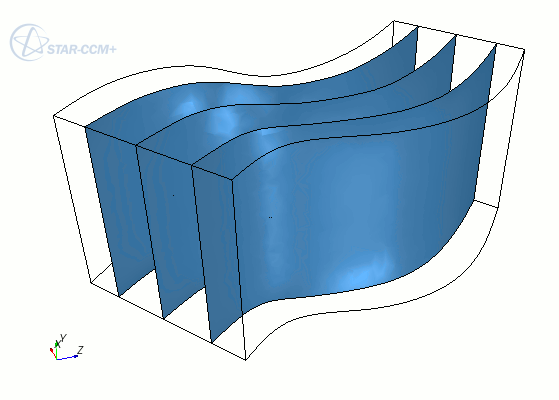
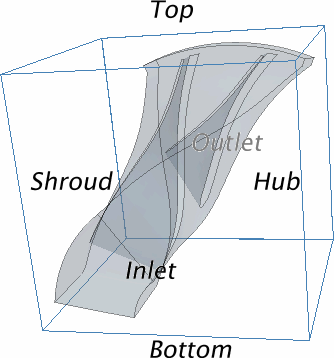
Block-Mapped Coordinate System
A block-mapped coordinate system is a type of user-defined coordinate system in Simcenter STAR-CCM+, that defines points based on evenly distributed gradations between selected end surfaces in a topological cube. Each coordinate direction has a range of 0 to 1, where [0, 0, 0] defines one corner of the cube, and [1, 1, 1] defines the diagonally opposite corner of the cube.