Axis Properties Reference
The Axes node appears in the node of any plot type, and contains sub-nodes for controlling the arrangement and appearance of axes.
Axes Node Properties
- Preferred X-Axis
- Selects the axis to be assigned to new data sets as the x-axis—bottom axis by default.
- Preferred Y-Axis
- Selects the axis to be assigned to new data sets as the y-axis—left axis by default.
Axes Node Action
These are the pop-up menu items available when you right-click the Axes node.
- New Axis
- Adds an axis to the plot if it is not already present, either Top or Right.
- Orient Axes
- Change the orientation of the axes. In the Orient Axes dialog, use any of the buttons to change the orientation of the axes:
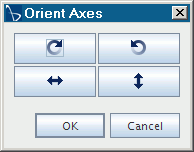
 -- rotates the plot clockwise 90 degrees
-- rotates the plot clockwise 90 degrees  -- rotates the plot counterclockwise 90 degrees
-- rotates the plot counterclockwise 90 degrees  -- flips the plot horizontally
-- flips the plot horizontally  -- flips the plot vertically
-- flips the plot vertically
[Cartesian] Axis Properties
Cartesian axes, the sub-nodes of the Axes node, are Left and Bottom in every plot type by default, and can be added as Top and/or Right through the use of the New Axis right-click menu action.
- Logarithmic
- Activate this property to make the axis logarithmic rather than linear.
- Minimum
- Adjust the value of this property and the Maximum to focus on a region of the plot.
- Lock Minimum
- Maximum
- Lock Maximum
- Range Mode
- Selects the method used for calculating the range applied to the axis when data is appended to the plot. The following modes are available:
- Data Bounds—the default setting. The viewable range is calculated so as to show the full range of data on the plot.
- Sliding Window—for monitor plots only. When chosen, a Sliding Window Options child node appears in which you set the Sliding Window Width. As new data is appended to the monitor plot, the view range updates so as to display points within the chosen window. This mode is indented for use in long-running transient simulations.
- Reverse
- When activated, causes the scale and the corresponding plot points to appear in the reverse order.
- Position
- Choose from among Left, Bottom, Right, and Top.
- Visible
- Deactivate this property to remove the axis from view.
[Cartesian] Axis Sub-Nodes: Title, Major Labels, and Minor Ticks
Each individual axis node contains sub-nodes for changing or removing the title and labels, major and minor ticks, and major and minor grid lines.
Title Properties
- Title
- Lock Title Name
- Rotation
- Choose from among increments of 90 degrees (starting at zero).
- Font
- Click
 (Custom Editor) to access the font control dialog.
(Custom Editor) to access the font control dialog. - Visible
- Deactivate this property to remove the title.
Note An empty string hides the title. No additional space is gained.
Major Labels Properties
- Font
- Click
 (Custom Editor) to access the font control dialog.
(Custom Editor) to access the font control dialog. - Precision
- Controls the maximum number of digits that appear after the decimal place in the axis labels.
- Auto Precision
- Pad Decimals
- Activate this property to add zeroes to empty decimals based on default decimal precision settings.
- Spacing
- Sets the spacing between axis labels in the units of the axis. For example, with a Minimum of 0.0 and a Maximum of 8.0, a label Spacing of 4.0 will place labels at 0.0, 4.0 and 8.0. Setting this value to 0.0 hides the tick labels.
- Auto Spacing
- Notation
- Selects the type of notation for the data labels, within the maximum number of digits specified in the Precision property:
- Best Fit—this option automatically chooses either decimal or scientific notation, whichever takes the least amount of space to achieve the requested precision. This is the default.
- Decimal—this option displays the full decimal values.
- Scientific—this option displays the values in scientific notation.
- Visible
- Deactivate this property to remove the labels.
Minor Ticks Properties
- Count
- Sets the number of minor ticks between the major labels.
- Visible
- Deactivate this property to remove the minor ticks.
Major Labels and Minor Ticks: Shared Grid Properties
- Grid Style
- For no grid line, specify None. Otherwise choose from options including Solid and Dash.
- Grid Color
- Specify RGB values using a comma to separate the numeric values. Alternatively, click
 (Custom Editor) to access the color control dialog. For details, see Defining Colors.
(Custom Editor) to access the color control dialog. For details, see Defining Colors. - Grid Width
- Grid Visible
- Deactivate this property to remove the grid lines.
Axis Type Properties
For controlling the display of data, the histogram plot includes the Axis Type node.
- Bins
- Sets the number of intervals along the x-axis (binning axis) of the histogram plot.
- Smooth Values
- When activated, uses node values in the display.
- Range Mode
- When set to Manual, activates the Range sub-node, in which you can specify the range.
- Weighting
- When set to Scalar Function, activates the Weighting sub-node so that you can customize the y-axis with a scalar function.
- Bin Spacing
- To control whether the bins are scaled logarithmically or not, choose from the following options:
- Tied to Axis—selects the bin spacing depending on whether the Logarithmic option of the x-axis is activated. This setting is the default for new histogram plots.
- Linear—distributes the data into evenly spaced bins. Older simulation files restored into the current version of Simcenter STAR-CCM+ have this setting by default, and therefore function the same as before.
- Logarithmic—distributes the data into evenly scaled bins. Logarthmic binning only works with positive, non-zero values. When the Range Mode property is set to Auto, negative range values are automatically rejected. When the property is set to Manual, take care to set the Range node to positive, non-zero values. Otherwise, Simcenter STAR-CCM+ generates a warning in the Output window that logarithmic binning cannot be performed.
Axis Type Sub-Nodes: Weighting, Range, and Bin
The Axis Type node contains sub-nodes to specify the details of how your histogram plot data is to be displayed.
Weighting Properties
- Field Function
- Selects a scalar function for the y-axis.
Range Properties
- Range
- Lets you enter minimum and maximum binning values.
Bin Properties
- Field Function
- Selects a scalar function for the x-axis.