Defining a Scalar Warp Surface
The scalar warp surface moves the point coordinates on the surface of its input parts along the point normal vectors by an amount equal to the scalar value times the scale factor.
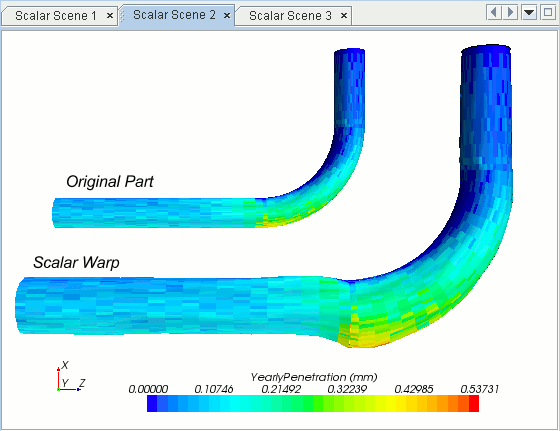
To create a scalar warp:
- Follow the general procedure outlined in the section, Defining Derived Parts General Workflow. Choose the menu option, .
- Specify the input parts and display option as described in the section, Defining Derived Parts General Workflow.
-
Complete the scalar warp definition by specifying the following properties:
- Scalar field — select the scalar field function as the basis for the warp surface. The list of available scalar field functions depends on the physics models that you selected.
You can specify the scalar field using the Scalar Field property, or the Scalar group box in the in-place dialog.
- Scale Factor — specify the factor by which the scalar field is multiplied.
You can specify the Scale Factor in the in-place dialog or the Properties window.
For more information on the available properties, see Scalar Warp Properties. - Scalar field — select the scalar field function as the basis for the warp surface. The list of available scalar field functions depends on the physics models that you selected.